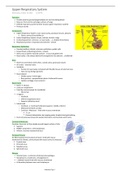
Upper Respiratory System
Wednesday, October 19, 2022 10:56 PM
Functions
• Provide area for gas exchange between air and circulating blood
• Move air from and to exchange surfaces of lungs
• Defend respiratory system & other tissues (upper respiratory system)
• Produce sounds
Components
1. Upper Respiratory System: nose, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx
a. Filters, warms & humidifies air
2. Lower Respiratory System: larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
3. Conducting portion: entrance → nasal cavity …→ smallest bronchioles
4. Respiratory portion: respiratory bronchioles + alveoli
Respiratory Epithelium
• Pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium, goblet cells
• Except finest conducting portions + alveoli
• Sticky mucus bathes exposed surfaces - mucous & goblet cells
• Nasal cavity: cilia sweeps debris/microorganisms into pharynx …swallowed
Nose
• Nose has connections with orbits, cranial cavity, paranasal sinuses
• Air enters - external nares
• Vestibule
○ Portion of nasal cavity contained with flexible tissues of external nose
○ Hairs to trap foreign particles
• Nasal septum
○ Divides cavity = left & right
○ Bony portion = perpendicular plate of ethmoid & vomer
○ Hyaline cartilage covers anterior
Nasal Cavity
• Nares → Choana
• Leads to nasopharynx
• Lined by mucosa except for [vestibule]
○ Skin & hair
• 3 regions
○ Vestibule
○ Inferior (respiratory area)
○ Superior (olfactory area)
• Lateral wall
○ Vestibule → Conchae/Turbinate (superior, middle, inferior)
○ Meatuses beneath conchae
○ Conchae + Meatuses - lined with mucous membrane
▪ ↑ S.A
▪ Prevents dehydration by trapping water droplets during breathing
• Ducts of paranasal sinuses & nasolacrimal ducts communicate with cavity
Conchae & Meatuses
Conchae: forces air to flow steady around largest surface of cilia
1. Superior
2. Middle: projections = ethmoidal bulla
3. Inferior: receives nasolacrimal duct
Paranasal Sinuses
Air filled cavities form by bones of skull - lined with mucus
membrane & ciliated, communicate with nasal cavity via meatuses
1. Frontal sinus
2. Ethmoid sinus
3. Maxillary sinus
4. Sphenoid sinus
Pharynx
• Internal nares → entrance of pharynx & esophagus
• Nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
• = skeletal muscle lined with mucous membrane
• At boundary between naso and oropharynx
Respiratory epithelium → Stratified squamous epithelium
Anatomy Page 1
Wednesday, October 19, 2022 10:56 PM
Functions
• Provide area for gas exchange between air and circulating blood
• Move air from and to exchange surfaces of lungs
• Defend respiratory system & other tissues (upper respiratory system)
• Produce sounds
Components
1. Upper Respiratory System: nose, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx
a. Filters, warms & humidifies air
2. Lower Respiratory System: larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
3. Conducting portion: entrance → nasal cavity …→ smallest bronchioles
4. Respiratory portion: respiratory bronchioles + alveoli
Respiratory Epithelium
• Pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium, goblet cells
• Except finest conducting portions + alveoli
• Sticky mucus bathes exposed surfaces - mucous & goblet cells
• Nasal cavity: cilia sweeps debris/microorganisms into pharynx …swallowed
Nose
• Nose has connections with orbits, cranial cavity, paranasal sinuses
• Air enters - external nares
• Vestibule
○ Portion of nasal cavity contained with flexible tissues of external nose
○ Hairs to trap foreign particles
• Nasal septum
○ Divides cavity = left & right
○ Bony portion = perpendicular plate of ethmoid & vomer
○ Hyaline cartilage covers anterior
Nasal Cavity
• Nares → Choana
• Leads to nasopharynx
• Lined by mucosa except for [vestibule]
○ Skin & hair
• 3 regions
○ Vestibule
○ Inferior (respiratory area)
○ Superior (olfactory area)
• Lateral wall
○ Vestibule → Conchae/Turbinate (superior, middle, inferior)
○ Meatuses beneath conchae
○ Conchae + Meatuses - lined with mucous membrane
▪ ↑ S.A
▪ Prevents dehydration by trapping water droplets during breathing
• Ducts of paranasal sinuses & nasolacrimal ducts communicate with cavity
Conchae & Meatuses
Conchae: forces air to flow steady around largest surface of cilia
1. Superior
2. Middle: projections = ethmoidal bulla
3. Inferior: receives nasolacrimal duct
Paranasal Sinuses
Air filled cavities form by bones of skull - lined with mucus
membrane & ciliated, communicate with nasal cavity via meatuses
1. Frontal sinus
2. Ethmoid sinus
3. Maxillary sinus
4. Sphenoid sinus
Pharynx
• Internal nares → entrance of pharynx & esophagus
• Nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
• = skeletal muscle lined with mucous membrane
• At boundary between naso and oropharynx
Respiratory epithelium → Stratified squamous epithelium
Anatomy Page 1