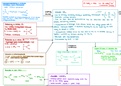
Nttztcl
-
Halogen◦alkanet excess R -
Ntlz + tea → R -
ethanolice conc ammonia R ammonium chloride
-
heat sealed container
Amine-halogenoa.I .
÷µ., →
Ñ + cttzctlzBr-octb.CH N'
"
2
making A NRZ detergent nucle -
.
3)
>
"
" "
" y, 4µg """
°ⁿiⁿˢ
ammonium ion "+
+ N""Br can be Primary secondary tertiary wonderment "'
_
-
> '
Problem : mixture
Aliphatic without benzene cts
of primary secondary
,
etc since amines
.
- -
have lone pair : take part in NS reactions with
-
_
Due to lone pair of electrons on the N amines can act
halogenoalbnaneg .
as
bases
, accepting protons
RegañtnU① _
propyl amine is stronger than amine since the
alkyl group has a
-
Use LiAlH4 in
dry ether followed >
positive inductive affect ↑ electron
density on the N
meaning
its more
by dilute acid
it " likely to accept a proton
/
R -
C _=N +4Gt] -0 A C N is donated into the
lone pair on the N
phenylamine weaker since the
-
a
-
-
¥
"
H the N
Problem :
expensive system decreasing electron density
,
on .
-
amines are nucleophiles
Reduction of nitrile ② ( catalytic hydrogenation
a z
Hydrogen gas, nickel catalyst , high
-
a
temp + pressure
↑ ✓H nucleophilic
CIN 2112 → ✓
§ My
+ _
substitution
copper CID ions →
complexion
✓
Blue Pale blue Ppt
Acyl chloride -1 amine
Cultlzo) ,
2-1
Reduce a nitro compound @ (0*2)/+
1) Heat nitrocompound tint cone HCl under Ctf c=°+ a- butyl amie solution
reflux ↳NH ,
-
, a-↳
HCl
→ -
+
→ salt ( add sodium hydroxide) µ '
N H
- facts as base
taking
1 s
Noz MHz einanoyi methylamine
4-13
two 1-1-1 from complex
chloride W
+ GCH] →
I +2420 f
meinyietnanamide
Id
Amide + dit tha
-
-
to
v -
o
° ←°
✗ su
"° " " "" →
Ctfz -
C. + *" "
" -
+
" OH
e
-
carbonyl group pulls electrons
away from the
Ntfz say
acid rest of the CONHZ group
-
small amides soluble in water (HB)
-
Halogen◦alkanet excess R -
Ntlz + tea → R -
ethanolice conc ammonia R ammonium chloride
-
heat sealed container
Amine-halogenoa.I .
÷µ., →
Ñ + cttzctlzBr-octb.CH N'
"
2
making A NRZ detergent nucle -
.
3)
>
"
" "
" y, 4µg """
°ⁿiⁿˢ
ammonium ion "+
+ N""Br can be Primary secondary tertiary wonderment "'
_
-
> '
Problem : mixture
Aliphatic without benzene cts
of primary secondary
,
etc since amines
.
- -
have lone pair : take part in NS reactions with
-
_
Due to lone pair of electrons on the N amines can act
halogenoalbnaneg .
as
bases
, accepting protons
RegañtnU① _
propyl amine is stronger than amine since the
alkyl group has a
-
Use LiAlH4 in
dry ether followed >
positive inductive affect ↑ electron
density on the N
meaning
its more
by dilute acid
it " likely to accept a proton
/
R -
C _=N +4Gt] -0 A C N is donated into the
lone pair on the N
phenylamine weaker since the
-
a
-
-
¥
"
H the N
Problem :
expensive system decreasing electron density
,
on .
-
amines are nucleophiles
Reduction of nitrile ② ( catalytic hydrogenation
a z
Hydrogen gas, nickel catalyst , high
-
a
temp + pressure
↑ ✓H nucleophilic
CIN 2112 → ✓
§ My
+ _
substitution
copper CID ions →
complexion
✓
Blue Pale blue Ppt
Acyl chloride -1 amine
Cultlzo) ,
2-1
Reduce a nitro compound @ (0*2)/+
1) Heat nitrocompound tint cone HCl under Ctf c=°+ a- butyl amie solution
reflux ↳NH ,
-
, a-↳
HCl
→ -
+
→ salt ( add sodium hydroxide) µ '
N H
- facts as base
taking
1 s
Noz MHz einanoyi methylamine
4-13
two 1-1-1 from complex
chloride W
+ GCH] →
I +2420 f
meinyietnanamide
Id
Amide + dit tha
-
-
to
v -
o
° ←°
✗ su
"° " " "" →
Ctfz -
C. + *" "
" -
+
" OH
e
-
carbonyl group pulls electrons
away from the
Ntfz say
acid rest of the CONHZ group
-
small amides soluble in water (HB)