Psychology and the Brain: Week 1
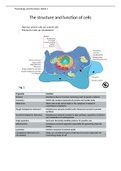
The structure and function of cells
- Nervous system cells are animal cells
- Filaments make up cytoskeleton
-
,Psychology and the Brain: Week 1
Specialised cells in nervous systems:
- Neurons amin cells used in signalling
- Glia cells divides into different types of cells
- Oligodendrocytes and Schwann have similar functions but cells differ in locations (in
CNS and peripheral NS)
- Oligodendrocytes in CNS
- Schwann cells in PNS
Specialised
cells in
Nervous
System
Glia Neuron
Ependymal
Macroglia Microglia Satellite cells
cells
Oligodendrocytes
OR Astrocytes
Schwann cells
Macroglia cells- star cells (astrocyte):
- Image shown cell stained with fluorescent markers
The astrocyte, named after its star like structure is one type of
macroglia. These cells have several important functions including:
• Regulating local supply of oxygen and glucose to neurons.
• Providing structural support and stability to neurons.
• Mopping up leaked or excessive chemical messengers
(neurotransmitters).
• Regulating the concentration of potassium ions (K+).
They also appear to have a fundamental role in brain signalling
research still trying to support this
Macroglia cells- Insulating cells:
The oligodendrocyte - second type of macroglia found in the central nervous system.
Schwann cell-Its counterpart in the peripheral nervous system is the.
, Psychology and the Brain: Week 1
These cells have several important functions including:
• Form rows of semi-rigid tissue between neurons which is believed to provide
structural support.
• Supply nutrients to neurons.
• Provide myelin sheaths-insulating/fatty layer surrounding neurons
Microglia-smalls cells:
- The second major class of glia cells
Microglia have a range of functions including:
• Acting as brain scavengers (macrophages) engulfing and destroying
bacteria and debris from dead and dying neurons and glia.
• Remodelling the nervous system during development
• Secreting chemicals important in glial cell and blood vessel formation
• Responding to immune system activation and neurodegeneration
Image shows when microglia cells are activated:
- Left image- shows resting state of cells
- When the brain takes damage, cells become activated to perform
function as brain scavengers (right image)
Other glia cells:
Ependymal cells
- form a layer lining the brain ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord.
- They are one of the sources of CSF
- they secrete it and may assist in its circulation.
Satellite cells
- surround sensory neurons in the PNS
The structure and function of cells
- Nervous system cells are animal cells
- Filaments make up cytoskeleton
-
,Psychology and the Brain: Week 1
Specialised cells in nervous systems:
- Neurons amin cells used in signalling
- Glia cells divides into different types of cells
- Oligodendrocytes and Schwann have similar functions but cells differ in locations (in
CNS and peripheral NS)
- Oligodendrocytes in CNS
- Schwann cells in PNS
Specialised
cells in
Nervous
System
Glia Neuron
Ependymal
Macroglia Microglia Satellite cells
cells
Oligodendrocytes
OR Astrocytes
Schwann cells
Macroglia cells- star cells (astrocyte):
- Image shown cell stained with fluorescent markers
The astrocyte, named after its star like structure is one type of
macroglia. These cells have several important functions including:
• Regulating local supply of oxygen and glucose to neurons.
• Providing structural support and stability to neurons.
• Mopping up leaked or excessive chemical messengers
(neurotransmitters).
• Regulating the concentration of potassium ions (K+).
They also appear to have a fundamental role in brain signalling
research still trying to support this
Macroglia cells- Insulating cells:
The oligodendrocyte - second type of macroglia found in the central nervous system.
Schwann cell-Its counterpart in the peripheral nervous system is the.
, Psychology and the Brain: Week 1
These cells have several important functions including:
• Form rows of semi-rigid tissue between neurons which is believed to provide
structural support.
• Supply nutrients to neurons.
• Provide myelin sheaths-insulating/fatty layer surrounding neurons
Microglia-smalls cells:
- The second major class of glia cells
Microglia have a range of functions including:
• Acting as brain scavengers (macrophages) engulfing and destroying
bacteria and debris from dead and dying neurons and glia.
• Remodelling the nervous system during development
• Secreting chemicals important in glial cell and blood vessel formation
• Responding to immune system activation and neurodegeneration
Image shows when microglia cells are activated:
- Left image- shows resting state of cells
- When the brain takes damage, cells become activated to perform
function as brain scavengers (right image)
Other glia cells:
Ependymal cells
- form a layer lining the brain ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord.
- They are one of the sources of CSF
- they secrete it and may assist in its circulation.
Satellite cells
- surround sensory neurons in the PNS