https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dniCgjsgMv8
Kidneys have 3 majors functions:
1. Excretion of waste
2. Maintenance of extracellular fluid (ECF) volume and
composition
3. Hormone synthesis
Why are renal function tests necessary?
- Identify renal dysfunction
- Diagnose renal disease
- Monitor disease progress
- Monitor response to treatment
- Assess changes in function that may impact on therapy
Kidneys function tests:
1. Filtering capability of kidneys - glomerular filtration
rate (GFR)
2. Presence of disease markers in urine
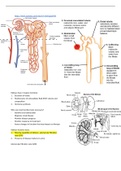
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
, - Volume of plasma from which a given substance is completely removed by glomerular filtration in a given time
- Estimation of efficiency
- 140ml/min in healthy adults
- Identifies chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Measured using exogenous or endogenous substances
Measurement of GFR: characteristics of an ideal substance to measure GFR
- Stable concentration in plasma
- Physiologically inert
- Freely filtered at the glomerulus
- Not secreted, reabsorbed, synthesised or metabolised by kidneys
Exogenous substances to measure GFR Endogenous substances to measure GFR - Serum creatinine:
1. Radioisotopes: 1. Advantages:
a. 125I-iothalamate a. Product of muscle breakdown
b. 51Cr-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid b. Freely filtered by glomerulus
(EDTA) 2. Disadvantages:
c. 99mTc-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic a. Timed urine collection
acid (99mTc DTPA) b. Plasma creatinine affected by age, sex, exercise, muscle mass,
2. Non-radioisotopic: certain drugs and nutrition
a. Inulin c. Increased tubular secretion of creatinine in renal insufficiency
b. Iohexol d. Extrarenal clearance in advanced kidney disease
e. Usually overestimated by 10-40% at clearances > 80ml/min
(100ml/min)
Don’t rely on serum creatinine clearance measurement alone to assess kidney function
Estimate GFR (eGFR):
- A more reliable estimate of GFR than using serum creatinine clearance alone
- Cockcroft and Gault Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) (adults)
- Schwartz and Counahan-Barratt equation (children)
- UK department of health recommends use of MDRD in addition to serum creatinine
- Only suitable if kidney function is stable
Calculate the creatinine clearance in ml/min: A patient produced 1500ml of urine in a 24 hour
period. This patient had a urine creatinine concentration of 10mmol/L and a plasma creatinine
concentration of 100 umol/L. Calculate the creatinine clearance in ml/min.
Kidneys function tests:
1. Filtering capability of kidneys - glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
2. Presence of disease markers in urine
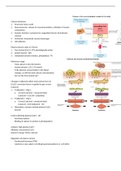
Presence of disease markers in urine:
- Urinalysis: colour, turbidity, foaming
- Microscopic analysis
Kidneys have 3 majors functions:
1. Excretion of waste
2. Maintenance of extracellular fluid (ECF) volume and
composition
3. Hormone synthesis
Why are renal function tests necessary?
- Identify renal dysfunction
- Diagnose renal disease
- Monitor disease progress
- Monitor response to treatment
- Assess changes in function that may impact on therapy
Kidneys function tests:
1. Filtering capability of kidneys - glomerular filtration
rate (GFR)
2. Presence of disease markers in urine
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
, - Volume of plasma from which a given substance is completely removed by glomerular filtration in a given time
- Estimation of efficiency
- 140ml/min in healthy adults
- Identifies chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Measured using exogenous or endogenous substances
Measurement of GFR: characteristics of an ideal substance to measure GFR
- Stable concentration in plasma
- Physiologically inert
- Freely filtered at the glomerulus
- Not secreted, reabsorbed, synthesised or metabolised by kidneys
Exogenous substances to measure GFR Endogenous substances to measure GFR - Serum creatinine:
1. Radioisotopes: 1. Advantages:
a. 125I-iothalamate a. Product of muscle breakdown
b. 51Cr-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid b. Freely filtered by glomerulus
(EDTA) 2. Disadvantages:
c. 99mTc-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic a. Timed urine collection
acid (99mTc DTPA) b. Plasma creatinine affected by age, sex, exercise, muscle mass,
2. Non-radioisotopic: certain drugs and nutrition
a. Inulin c. Increased tubular secretion of creatinine in renal insufficiency
b. Iohexol d. Extrarenal clearance in advanced kidney disease
e. Usually overestimated by 10-40% at clearances > 80ml/min
(100ml/min)
Don’t rely on serum creatinine clearance measurement alone to assess kidney function
Estimate GFR (eGFR):
- A more reliable estimate of GFR than using serum creatinine clearance alone
- Cockcroft and Gault Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) (adults)
- Schwartz and Counahan-Barratt equation (children)
- UK department of health recommends use of MDRD in addition to serum creatinine
- Only suitable if kidney function is stable
Calculate the creatinine clearance in ml/min: A patient produced 1500ml of urine in a 24 hour
period. This patient had a urine creatinine concentration of 10mmol/L and a plasma creatinine
concentration of 100 umol/L. Calculate the creatinine clearance in ml/min.
Kidneys function tests:
1. Filtering capability of kidneys - glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
2. Presence of disease markers in urine
Presence of disease markers in urine:
- Urinalysis: colour, turbidity, foaming
- Microscopic analysis