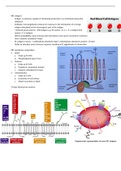
RBC antigens
- Antigen: A substance capable of stimulating production in an individual lacking that
substance
- Antibody: Immunoglobulin produced in response to the introduction of a foreign
antigen stimulated by the immunogenic part of the antigen.
- >36 blood group systems, >300 antigens e.g. Rh system = D, C, c, E, e antigens Kell
system = K, k antigens
- ABO incompatibility causes intravascular haemolysis (most severe transfusion reactions)
- Only 9 systems considered ‘Major’
- RC antigens may be: - Carbohydrate attached to lipid - Carbohydrate attached to protein - Protein
- Ability to stimulate severe immune response resulting in RC agglutination & destruction
RBC membrane composition
1. Lipids:
a. Make up 40-44%
b. Phospholipid bi-layer (7nm)
2. Proteins:
a. Make up 49-52%
b. Peripheral: cytoplasmic domain
c. Integral: embedded in bi-layer
3. Carbohydrates:
a. Make up 5-10%
b. Exclusively on cell surface
c. Attach to proteins or lipids
9 Major blood group systems:
, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9O5JQqlngFY
ABO inheritance
- Inherit 2 alleles from a possible 3…
- The A & B alleles are DOMINANT
- The O allele is recessive
- The A & B alleles are CODOMINANT
- TWO ‘O’ alleles must be inherited to express phenotype of group O
Alleles code for an ENZYME that allows the ATTACHMENT of the A or B antigens to the H antigen already present on
the RC membrane
- H antigen is present in 99.9% of all populations, those who do not express the H antigen produce anti-H antibodies
& are referred to as Bombay phenotype
- If A allele is present, the enzyme ‘A-transferase’ converts the H antigen into the A antigen
- If B allele is present, ‘B-transferase’ converts the H antigen into the B antigen
- If O allele is present, there is no enzyme produced so the H antigen remains unchanged = Group O
Anti-A & Anti-B antibodies:
- IgM - Naturally occurring (≥4 months)
- Capable of causing intravascular haemolysis
Group O:
- Caused by frameshift mutations in A or B transferase gene that causes loss of enzyme activity
- Cannot convert H antigen into A or B antigen
ABO system
- Antigen: A substance capable of stimulating production in an individual lacking that
substance
- Antibody: Immunoglobulin produced in response to the introduction of a foreign
antigen stimulated by the immunogenic part of the antigen.
- >36 blood group systems, >300 antigens e.g. Rh system = D, C, c, E, e antigens Kell
system = K, k antigens
- ABO incompatibility causes intravascular haemolysis (most severe transfusion reactions)
- Only 9 systems considered ‘Major’
- RC antigens may be: - Carbohydrate attached to lipid - Carbohydrate attached to protein - Protein
- Ability to stimulate severe immune response resulting in RC agglutination & destruction
RBC membrane composition
1. Lipids:
a. Make up 40-44%
b. Phospholipid bi-layer (7nm)
2. Proteins:
a. Make up 49-52%
b. Peripheral: cytoplasmic domain
c. Integral: embedded in bi-layer
3. Carbohydrates:
a. Make up 5-10%
b. Exclusively on cell surface
c. Attach to proteins or lipids
9 Major blood group systems:
, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9O5JQqlngFY
ABO inheritance
- Inherit 2 alleles from a possible 3…
- The A & B alleles are DOMINANT
- The O allele is recessive
- The A & B alleles are CODOMINANT
- TWO ‘O’ alleles must be inherited to express phenotype of group O
Alleles code for an ENZYME that allows the ATTACHMENT of the A or B antigens to the H antigen already present on
the RC membrane
- H antigen is present in 99.9% of all populations, those who do not express the H antigen produce anti-H antibodies
& are referred to as Bombay phenotype
- If A allele is present, the enzyme ‘A-transferase’ converts the H antigen into the A antigen
- If B allele is present, ‘B-transferase’ converts the H antigen into the B antigen
- If O allele is present, there is no enzyme produced so the H antigen remains unchanged = Group O
Anti-A & Anti-B antibodies:
- IgM - Naturally occurring (≥4 months)
- Capable of causing intravascular haemolysis
Group O:
- Caused by frameshift mutations in A or B transferase gene that causes loss of enzyme activity
- Cannot convert H antigen into A or B antigen
ABO system