Physiology notes
Part of the brain related to smell:
- Cortex (human/chimpanzee)
- Whole brain (dolphin)
- Cerebellum (cat/dolphin)
- Bulbus olfactorius (rat/rabbit)
Dolphins have 2 brains, when sleeping one brain is active.
History of brain research
Trepanation:
- Therapy: making holes in the skull to let evil spirits out
- To kill or cure: curing psychiatric diseases.
Hippocrates
- Correlation between structure and function (all sensory organs on
the head)
- Eyes, ears, nose, tongue with connecting nerves: the brain is the
organ of sensation
- Site of intelligence
Aristoteles:
- Heart is the intellectual centre.
- Brain serves to cool the passions of the heart
Galenus:
- Physician of the gladiators and performed animal dissections
- Cerebrum: sensory system (because of the soft structure)
- Cerebellum: muscle control (because of the solid structure)
- Idea that body functions are controlled by body fluids.
Descartes: made a hydraulic system (fluid is used to move energy).
Phrenology: skull shape and size (the outside)
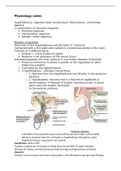
Anatomy of the brain
Homunculus: motoric part of the brain. Controls the body (feet, hands,
mouth etc.)
There is flexibility of the brain, it can learn new things and functions.
Details of cortical map (brain) structure are largely created and altered by
experience. Because of the memory of the brain, amputated body parts
can still be felt (phantom pain).
Cerebral cortex
3 specializations:
Sensory areas
o Sensory input translated into perception. Responsible for
receiving and interpreting sensory information from different
parts of the body.
Association areas
o Integrate information from sensory and motor areas can direct
voluntary behaviours.
Motor areas
o Direct skeletal muscle movement
, Frontal lobe: personality, association area. Decides what to do.
Lobotomy: therapy for unrestrained behaviour. Neurosurgical treatment
in the brain’s prefrontal cortex where it is disconnected.
Broca’s area: important to produce speech in the left frontal lobe.
Wernicke’s area: interpreting and understanding language.
Cerebral lateralization: one area in the brain takes the function (e.g., left
side) other are of the brain takes another function.
Brain stem: reflex mechanisms
Cerebellum: motor control (equilibrium, muscles, walking)
Cerebrum (frontal brain):
o Cerebral cortex = higher brain functions (language)
o Hypothalamus = integration of hormonal & metabolic signals
with autonomic processes and higher brain functions
o Hippocampus = learning and memory
o Amygdala = emotion, conditioned responses
All of this is connected via neuronal networks = modulator of sensory and
cognitive processes. Neurons known as diffuse modulatory systems.
4 modulatory systems:
1. Adrenergic
2. Serotonergic
3. Dopaminergic
4. Cholinergic
Part of the brain related to smell:
- Cortex (human/chimpanzee)
- Whole brain (dolphin)
- Cerebellum (cat/dolphin)
- Bulbus olfactorius (rat/rabbit)
Dolphins have 2 brains, when sleeping one brain is active.
History of brain research
Trepanation:
- Therapy: making holes in the skull to let evil spirits out
- To kill or cure: curing psychiatric diseases.
Hippocrates
- Correlation between structure and function (all sensory organs on
the head)
- Eyes, ears, nose, tongue with connecting nerves: the brain is the
organ of sensation
- Site of intelligence
Aristoteles:
- Heart is the intellectual centre.
- Brain serves to cool the passions of the heart
Galenus:
- Physician of the gladiators and performed animal dissections
- Cerebrum: sensory system (because of the soft structure)
- Cerebellum: muscle control (because of the solid structure)
- Idea that body functions are controlled by body fluids.
Descartes: made a hydraulic system (fluid is used to move energy).
Phrenology: skull shape and size (the outside)
Anatomy of the brain
Homunculus: motoric part of the brain. Controls the body (feet, hands,
mouth etc.)
There is flexibility of the brain, it can learn new things and functions.
Details of cortical map (brain) structure are largely created and altered by
experience. Because of the memory of the brain, amputated body parts
can still be felt (phantom pain).
Cerebral cortex
3 specializations:
Sensory areas
o Sensory input translated into perception. Responsible for
receiving and interpreting sensory information from different
parts of the body.
Association areas
o Integrate information from sensory and motor areas can direct
voluntary behaviours.
Motor areas
o Direct skeletal muscle movement
, Frontal lobe: personality, association area. Decides what to do.
Lobotomy: therapy for unrestrained behaviour. Neurosurgical treatment
in the brain’s prefrontal cortex where it is disconnected.
Broca’s area: important to produce speech in the left frontal lobe.
Wernicke’s area: interpreting and understanding language.
Cerebral lateralization: one area in the brain takes the function (e.g., left
side) other are of the brain takes another function.
Brain stem: reflex mechanisms
Cerebellum: motor control (equilibrium, muscles, walking)
Cerebrum (frontal brain):
o Cerebral cortex = higher brain functions (language)
o Hypothalamus = integration of hormonal & metabolic signals
with autonomic processes and higher brain functions
o Hippocampus = learning and memory
o Amygdala = emotion, conditioned responses
All of this is connected via neuronal networks = modulator of sensory and
cognitive processes. Neurons known as diffuse modulatory systems.
4 modulatory systems:
1. Adrenergic
2. Serotonergic
3. Dopaminergic
4. Cholinergic