Topic 3 – Infection and response
Table of Content
3.1 Communicable diseases.................................................... 2
3.1.1 Communicable (infectious) diseases...........................................................................2
3.1.2 Viral diseases ..............................................................................................................2
3.1.3 Bacterial diseases ........................................................................................................3
3.1.4 Fungal diseases ...........................................................................................................3
3.1.5 Protist diseases ...........................................................................................................4
3.1.6 Human defence systems .............................................................................................4
3.1.7 Vaccination .................................................................................................................5
3.1.8 Antibiotics and painkillers ...........................................................................................5
3.1.9 Discovery and development of drugs .........................................................................5
3.2 Monoclonal antibodies (biology only) (HT only) ................ 6
3.2.1 Producing monoclonal antibodies ..............................................................................6
3.2.2 Uses of monoclonal antibodies ...................................................................................7
3.3 Plant disease (biology only) .............................................. 7
3.3.1 Detection and identification of plant diseases ...........................................................7
3.3.2 Plant defence responses .............................................................................................8
1
, AQA GCSE Biology notes Topic 3 – Infection and response
3.1 Communicable diseases
3.1.1 Communicable (infectious) diseases
Pathogens • Microorganisms that cause communicable diseases
• Eg bacteria, viruses, protists, fungi
How cause? Bacteria • Produce toxins - damage tissues - ill
• Reproduce rapidly in binary fusion
Viruses • Live & reproduce rapidly inside cell - cell damage
How By air • Droplet infection
spread? • Ppl sneeze - expel droplet with pathogens from breathing system - other
ppl breath in
By water • Dirty water - cholera
Direct • Cuts - give excess to blood eg HIV
contact • Shake hands
How 1. Wash hands
prevent? 2. Drink clean water
3. Good hygiene
4. Isolate infected individuals
5. Destroy / control vectors eg mosquitoes
6. Vaccination
What is pandemic? (1)
• A disease affecting ppl in many countries
3.1.2 Viral diseases
Measles
Spread by • Inhalation of droplets from coughs/sneezes
Symptoms • Fever, red skin rash
• (serious - blindness, brain damage, fatal)
Prevention • Vaccination
• Isolate infected individuals
HIV/AIDs
Spread by • Exchange of body fluids eg blood when share needles
• Unprotected sexual contact with infected person
Symptoms • Flu-like illness
• Virus attack & remain hidden in immune system
• AIDs (last stage of HIV) occurs when immune system becomes so badly damaged - X
deal with other infections
Treatment • Antiretroviral drugs to control attack
Prevention • Use condoms
• Don't share needles
2
, AQA GCSE Biology notes Topic 3 – Infection and response
• Use HIV +ve mother bottle to feed children
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
Spread by • Contact between healthy & infected plants & vectors
Symptoms • Give distinctive 'mosaic' pattern of discoloration on leaves coz viruses destroy cells
How affect • Less chlorophyll - less photosynthesis - less glucose
growth of • A) Less respiration - less energy released for growth
plants? • B) Less amino acids/cellulose for growth
Prevention • Good field hygiene
• Good pest control
• Wash tools
All viral diseases - no treatment
3.1.3 Bacterial diseases
Salmonella food poisoning
Caused by • Food prepared in unhygienic condition - food contaminated with salmonella from raw
meat
• Eat uncooked food - bacteria not killed by heat
Spread by • Bacteria ingested in food - disrupt balance of natural gut bacteria
Symptoms • Fever, abdominal cramps, vomiting & diarrhoea
• 8-72hrs
Prevention • Vaccination
• Cook meat thoroughly
• Keep raw meat away from cooked food
• Avoid washing raw meat - spread bacteria around kitchen
Gonorrhoea - sexually transmitted disease (STD)
Spread by • Unprotected sexual contact with infected person
Symptoms • Thick yellow / green discharge from vagina / penis
• Pain on urinating
Prevention • Use condom
• Reduce no of sexual partners
• Antibiotics
Treatment • Antibiotic penicillin
3.1.4 Fungal diseases
Rose black spot
Spread • In environment by wind & water
Symptoms • Purple / black spots develop on leaves
• Weaken plant & affect growth coz reduce area available for photosynthesis - turns
yellow & drop early
Treatment • Use fungicides
3
, AQA GCSE Biology notes Topic 3 – Infection and response
Prevention • Remove / burn affected leaves / stems
3.1.5 Protist diseases
Malaria
Spread by • Mosquitos (act as vectors coz they transmit disease)
Symptoms • Recurrent episode of fever
• Fatal
• Shaking when protists burst out of blood cells
• Headaches, vomiting, diarrhoea
Treatment • Take antimalarial drugs - kill parasites in blood
Prevention • Use mosquito nets - avoid being bitten
• Insecticides - kill mosquitoes
• Remove standing water - prevent mosquitoes breeding
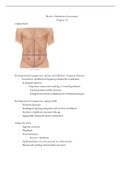
3.1.6 Human defence systems
Non-specific defence system
Skin • Acts as barrier
• Produces antimicrobial secretions - kill bacteria
Nose • Hair & mucus trap & prevent pathogens entering lungs
Trachea & bronchi • Has mucus - trap pathogens
• Cilia waft mucus upwards to throat - shallowed
Stomach • Produce HCl - kill pathogens in food
White blood cell
• Phagocytes (non-specific) & Lymphocytes (specific)
How?
1. Ingest pathogens (phagocytes)
• Phagocytes move towards, changes shape, attack pathogen, engulfs & digest it with enzymes
2. Produce antibodies (protein) (made by lymphocytes)
• Have complementary shape - specific antibody for specific pathogen
• Allow binding with antigens (foreign microorganisms)
• If same pathogen re-enters body, WBC respond quickly, produce correct antibodies, prevent
infection
3. Produce antitoxins - counteract toxins
4