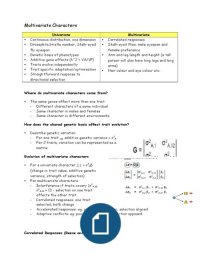
Mendel studied 7 characteristics (fig 2.4):
1. Height
2 Medelian inheritance 2. Flower color
3. Flower position
4. Seed color
2.1 Mendel’s study of pea plants 5. Seed shape
6. Pod color
Mendel chose pea plants as his experimental organism (fig 2.3)
7. Pod shape
Hybridization= breeding/ crossing between 2 individuals that have different characteristics.
Hybrid= offspring obtained from hybridization experiment.
Mendel: chose the garden pea (Pisum sativum) to study the natural laws governing plants hybrids-> garden pea was
advantageous because:
1. It had several varieties (height, flower appearance, seeds+ pods).
2. Easy crosses where the choice of parental plants could be controlled.
Mendel carried out 2 types of crosses:
1. Self-fertilization= involves the union of male+ female gametes derived from the same parent (natural).
2. Cross-fertilization= male+ female gametes from separate individuals (removing+ manipulating anthers).
Mendel studied seven characteristics that bred true (fig 2.4)
Character= general characteristic (e.g., eye color).
Trait/ variant= characteristics of an organism/ specific properties of a character (e.g., blue eye color).
True-breeding line/ strain= strain of a particular species that continues to produce the same trait after
several generations of self-fertilization (plants)/ inbreeding.
2.2 Law of segregation
Single-factor cross= cross in which an experimenter is following the outcome of only a single character.
Monohybrids= individual produced from a single-factor cross; parents had different variants for 1 character.
Parental generation (P generation)= 1st generation in the experiment (in a genetic cross).
F1 generation= offspring produced from a cross of a parental generation.
F2 generation= offspring produced from a cross/ self-fertilization of the F1 generation.
EXPERIMENT 2A: Mendel followed the outcome of a single character for two
generations (fig 2.5)
Mendel: didn’t have a hypothesis to explain the formation of hybrids; quantitative analysis of crosses may provide
mathematical relationships that govern hereditary traits.
Empirical approach= experiments are designed to determine quantitative relationships to derive laws that
govern biological, chemical/ physical phenomena-> to deduce empirical laws.
Mendel’s experiment: true breeding parental generation that differed in a single character.
Studied 7 characteristics; each showed 2 variants found in the same species (e.g., tall vs dwarf).
Crossed 2 variants of the same characteristic (monohybrid cross); 1 characteristic is observed.
Crossed 2 true breeding (homozygotic) plants: 1 dominant+ 1 recessive.
F1 via cross-fertilization (all Tt)+ F2 via self-fertilization of the F1 plants (TT+ 2Tt+ tt).
F2: phenotypic ratio 3:1 (tall: dwarf)-> genotypic ration 1:2:1.
INTERPRETING THE DATA
3 important ideas:
1. Data was against a blending mechanism: F1 had distinct traits that were like 1 of the 2 parents rather
intermediate traits-> 1 variant for a particular character is dominant over another variant.
Dominant= allele that determines the phenotype sin the heterozygous condition.
Recessive= trait/ gene that is masked by the presence of a dominant trait/ gene.
2. Particulate theory of inheritance= traits are inherited as discrete units that remain unchanged as they are
passed from parent to offspring (unit factors= genes)-> deduced from: F1 all dominant; F2 75% dominant.
3. 3:1 ration between dominant+ recessive trait : genes segregate from each other during the process that gives
rise to gametes.
1. Height
2 Medelian inheritance 2. Flower color
3. Flower position
4. Seed color
2.1 Mendel’s study of pea plants 5. Seed shape
6. Pod color
Mendel chose pea plants as his experimental organism (fig 2.3)
7. Pod shape
Hybridization= breeding/ crossing between 2 individuals that have different characteristics.
Hybrid= offspring obtained from hybridization experiment.
Mendel: chose the garden pea (Pisum sativum) to study the natural laws governing plants hybrids-> garden pea was
advantageous because:
1. It had several varieties (height, flower appearance, seeds+ pods).
2. Easy crosses where the choice of parental plants could be controlled.
Mendel carried out 2 types of crosses:
1. Self-fertilization= involves the union of male+ female gametes derived from the same parent (natural).
2. Cross-fertilization= male+ female gametes from separate individuals (removing+ manipulating anthers).
Mendel studied seven characteristics that bred true (fig 2.4)
Character= general characteristic (e.g., eye color).
Trait/ variant= characteristics of an organism/ specific properties of a character (e.g., blue eye color).
True-breeding line/ strain= strain of a particular species that continues to produce the same trait after
several generations of self-fertilization (plants)/ inbreeding.
2.2 Law of segregation
Single-factor cross= cross in which an experimenter is following the outcome of only a single character.
Monohybrids= individual produced from a single-factor cross; parents had different variants for 1 character.
Parental generation (P generation)= 1st generation in the experiment (in a genetic cross).
F1 generation= offspring produced from a cross of a parental generation.
F2 generation= offspring produced from a cross/ self-fertilization of the F1 generation.
EXPERIMENT 2A: Mendel followed the outcome of a single character for two
generations (fig 2.5)
Mendel: didn’t have a hypothesis to explain the formation of hybrids; quantitative analysis of crosses may provide
mathematical relationships that govern hereditary traits.
Empirical approach= experiments are designed to determine quantitative relationships to derive laws that
govern biological, chemical/ physical phenomena-> to deduce empirical laws.
Mendel’s experiment: true breeding parental generation that differed in a single character.
Studied 7 characteristics; each showed 2 variants found in the same species (e.g., tall vs dwarf).
Crossed 2 variants of the same characteristic (monohybrid cross); 1 characteristic is observed.
Crossed 2 true breeding (homozygotic) plants: 1 dominant+ 1 recessive.
F1 via cross-fertilization (all Tt)+ F2 via self-fertilization of the F1 plants (TT+ 2Tt+ tt).
F2: phenotypic ratio 3:1 (tall: dwarf)-> genotypic ration 1:2:1.
INTERPRETING THE DATA
3 important ideas:
1. Data was against a blending mechanism: F1 had distinct traits that were like 1 of the 2 parents rather
intermediate traits-> 1 variant for a particular character is dominant over another variant.
Dominant= allele that determines the phenotype sin the heterozygous condition.
Recessive= trait/ gene that is masked by the presence of a dominant trait/ gene.
2. Particulate theory of inheritance= traits are inherited as discrete units that remain unchanged as they are
passed from parent to offspring (unit factors= genes)-> deduced from: F1 all dominant; F2 75% dominant.
3. 3:1 ration between dominant+ recessive trait : genes segregate from each other during the process that gives
rise to gametes.