What YOU need to know for SDEN 2:
Wine IS:
85% water
13% alcohol (Fortified wines can go up to 22%)
2% acids, sugar, tannin
Fragrance & Flavour
Soil Types: Characteristic
Limestone, Kimmeridge, marl. Retains water and heat
Siliceous rock Water gets through very well. Rocks absorb heat very well and cool down slowly
at night.
Clay/Sand (mix) Lets water through, Small yield, High quality.
Clay Does not let water through well.
Humus Tannin rich wines.
Volcanic Soil (Basalt or Granite) Rich in minerals. Hard to work with.
Sand Lets water through. Finesse rich wines.
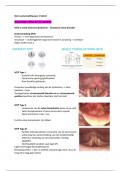
, Pruining Methods:
1. Guyot Method –
2. Cordon Method – Allows vines to be at a large distance , with the advamtage that the leave and bunber are well separated from each other to avoid fungal
diseases.
3. Gobelet Method – involves a free-standing vine, with a varying number of shoots which are all pruned back to about two buds.
White Grape Varieties:
1. Chardonnay
2. Chenin Blanc
3. Gewurztraminer
4. Gruner Veltliner
5. Pinot Blanc
6. Riesling
7. Sauvignon Blanc
8. Viognier
Red Wine Grape Varieties:
1. Cabernet Sauvignon
2. Gamay
3. Grenache
4. Malbec
5. Merlot
6. Pinot Noir
7. Sangiovese
8. Syrah
9. Tempranillo
Key Influencers:
, Grape Variety
Climate & Soil (Sun, Warmth & Humidity) (30-50 N&S from equator – best region for win plant to grow)
Vineyard
Winemaking
Cool Climate: Lighter Body, more acidity, less sugar, less alcohol
Hot Climate: Fuller Body, Less Acidity, more sugar, more alcohol.
What a vine needs to grow:
CO2 – for sugar
Sunlight – provides energy
Warmth -
Nutrients
Water
Wine Soil
Important Points:
- Composition
- Structure – not too tight or loose
- Water Balance
- Depth – generally a developed root system is necessary
- Nutrients
,
Wine IS:
85% water
13% alcohol (Fortified wines can go up to 22%)
2% acids, sugar, tannin
Fragrance & Flavour
Soil Types: Characteristic
Limestone, Kimmeridge, marl. Retains water and heat
Siliceous rock Water gets through very well. Rocks absorb heat very well and cool down slowly
at night.
Clay/Sand (mix) Lets water through, Small yield, High quality.
Clay Does not let water through well.
Humus Tannin rich wines.
Volcanic Soil (Basalt or Granite) Rich in minerals. Hard to work with.
Sand Lets water through. Finesse rich wines.
, Pruining Methods:
1. Guyot Method –
2. Cordon Method – Allows vines to be at a large distance , with the advamtage that the leave and bunber are well separated from each other to avoid fungal
diseases.
3. Gobelet Method – involves a free-standing vine, with a varying number of shoots which are all pruned back to about two buds.
White Grape Varieties:
1. Chardonnay
2. Chenin Blanc
3. Gewurztraminer
4. Gruner Veltliner
5. Pinot Blanc
6. Riesling
7. Sauvignon Blanc
8. Viognier
Red Wine Grape Varieties:
1. Cabernet Sauvignon
2. Gamay
3. Grenache
4. Malbec
5. Merlot
6. Pinot Noir
7. Sangiovese
8. Syrah
9. Tempranillo
Key Influencers:
, Grape Variety
Climate & Soil (Sun, Warmth & Humidity) (30-50 N&S from equator – best region for win plant to grow)
Vineyard
Winemaking
Cool Climate: Lighter Body, more acidity, less sugar, less alcohol
Hot Climate: Fuller Body, Less Acidity, more sugar, more alcohol.
What a vine needs to grow:
CO2 – for sugar
Sunlight – provides energy
Warmth -
Nutrients
Water
Wine Soil
Important Points:
- Composition
- Structure – not too tight or loose
- Water Balance
- Depth – generally a developed root system is necessary
- Nutrients
,