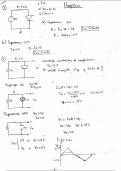
Oxidation is where an oxygen is gained and electrons are lost
Reduction is where oxygen is lost and electrons are gained
Iron is the most abundant element on Earth by mass and the fourth most abundant in the Earth’s
crust. It can be made into steel. These minerals form ores that can be dug out of the ground. This
means it can be extracted from a naturally occurring material.
A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its compounds. For example,
magnesium is more reactive than copper.
Potassium In ionic bonding, metal always loses electrons and non-electrons
Sodium gain.
Calcium
Magnesium Dye changes colour depending on the pH. A base is a substance that
Aluminium reacts with an acid to neutralise it and produce a salt.
Carbon
Alkali- substances producing more hydroxide ions OH - than hydrogen
Zinc
ions (H+) when dissolved in water.
Iron
Tin Acid- substances producing more hydrogen ions H+ than hydroxide
Lead ions (OH-) when in water.
Hydrogen
pH means the amount of hydrogen ions present in solution, universal
Copper
indicator give us a measure of this.
Silver
Gold Aq- aqueous (able to dissolve in water)
Platinum
Dissociate- split into smaller particles
Ionise- converting an atom into ion
Strong acid ionise completely in water. All acids particles dissociate to release H + ions
Weak acids do not fully ionise in solution. Only a small portion of acid particles dissociate to release
H+ ions
(Look in the book for signs)
Acid are sources of hydroxide ions H+. Alkali are source of hydroxide ions OH -. A neutralisation
reaction is a reaction between an acid and base. In acid-alkali neutralisation reaction, hydrogen ions
from the acid react with hydroxide ions from the alkali. H aq + OHaqH2Ol. When a salt reacts with a
metal, the products are a salt and hydrogen. In general: acid + metalsalt+ hydrogen salt
Hydrochloric Acid produces chloride salts. Nitric acid produces nitrate salts. Sulphuric acid produces
sulphate acid. A salt, water and carbon dioxide are produced when acids react with carbonates.
Acid + carbonate salt + water + carbon dioxide
Electrolysis is used to extract very reactive metals. If an ions is positive it is attracted towards a
cathode, cathode is negative. If an ion is negative it is attracted towards anode, anode is positive.
(PANIC). Anion is a negative ion while cation is a positive ion.
If the metal is above hydrogen in the reactivity series, hydrogen is formed at the cathode (no metal
is formed). If the metal is below hydrogen in the reactivity series the metal is formed. If there are
halides, e.g. chlorine, bromine (group 7) it will formed, if there are any other anion oxygen will form.
H2SO4-sulphuric acid
Reduction is where oxygen is lost and electrons are gained
Iron is the most abundant element on Earth by mass and the fourth most abundant in the Earth’s
crust. It can be made into steel. These minerals form ores that can be dug out of the ground. This
means it can be extracted from a naturally occurring material.
A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its compounds. For example,
magnesium is more reactive than copper.
Potassium In ionic bonding, metal always loses electrons and non-electrons
Sodium gain.
Calcium
Magnesium Dye changes colour depending on the pH. A base is a substance that
Aluminium reacts with an acid to neutralise it and produce a salt.
Carbon
Alkali- substances producing more hydroxide ions OH - than hydrogen
Zinc
ions (H+) when dissolved in water.
Iron
Tin Acid- substances producing more hydrogen ions H+ than hydroxide
Lead ions (OH-) when in water.
Hydrogen
pH means the amount of hydrogen ions present in solution, universal
Copper
indicator give us a measure of this.
Silver
Gold Aq- aqueous (able to dissolve in water)
Platinum
Dissociate- split into smaller particles
Ionise- converting an atom into ion
Strong acid ionise completely in water. All acids particles dissociate to release H + ions
Weak acids do not fully ionise in solution. Only a small portion of acid particles dissociate to release
H+ ions
(Look in the book for signs)
Acid are sources of hydroxide ions H+. Alkali are source of hydroxide ions OH -. A neutralisation
reaction is a reaction between an acid and base. In acid-alkali neutralisation reaction, hydrogen ions
from the acid react with hydroxide ions from the alkali. H aq + OHaqH2Ol. When a salt reacts with a
metal, the products are a salt and hydrogen. In general: acid + metalsalt+ hydrogen salt
Hydrochloric Acid produces chloride salts. Nitric acid produces nitrate salts. Sulphuric acid produces
sulphate acid. A salt, water and carbon dioxide are produced when acids react with carbonates.
Acid + carbonate salt + water + carbon dioxide
Electrolysis is used to extract very reactive metals. If an ions is positive it is attracted towards a
cathode, cathode is negative. If an ion is negative it is attracted towards anode, anode is positive.
(PANIC). Anion is a negative ion while cation is a positive ion.
If the metal is above hydrogen in the reactivity series, hydrogen is formed at the cathode (no metal
is formed). If the metal is below hydrogen in the reactivity series the metal is formed. If there are
halides, e.g. chlorine, bromine (group 7) it will formed, if there are any other anion oxygen will form.
H2SO4-sulphuric acid