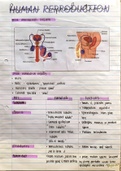
Plasma Membranes:
The structure and function of membranes
Factors affecting membrane structure
Diffusion
Active Transport
Osmosis
, The Structure and Function of Membranes
All biological membranes are composed mainly of lipid and protein molecules.
The three major types of lipids in cell membranes are:
- Phospholipids, which are the most abundant.
- Cholesterol, which is responsible for stabilising the membrane.
- Glycolipids, which are found at the external surface of the membrane.
The proteins within the membrane are largely concerned with the transport of molecules
across the membrane.
When phospholipid molecules are surrounded by a watery environment on all sides, they
group together to bury their hydrophobic tails while leaving their hydrophilic heads exposed
to water. They form a bilayer with the fatty acid chains positioned towards the non-aqueous
interior and the polar heads in contact with water. The lipid bilayer is, however, relatively
impermeable to many important molecules.
The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure
The fluid mosaic model describes
the double layer of phospholipids
with proteins penetrating this
layer. The proteins are globular
and form a mosaic in the fluid-like
lipid bilayer.
Glycoproteins and glycolipids form
part of the external structure of
the membrane.
Cholesterol molecules are positioned within the bilayer close to the fatty acid chains; these
molecules partially immobilise these chains and help to stabilise the membrane.
Extrinsic proteins:
- On surface or partially embedded.
- Give mechanical support and act as cell recognition sites/receptors.
- Sometimes called ‘Peripheral membrane proteins’
Intrinsic proteins:
- Completely span the bilayer.
- They are water filled tubes that allow water solube ions to diffuse across.
- Carrier proteins bind to ions or water-soluble molecules like glucose and amino acids and
then change shape in order to move these proteins across the membrane.
- Enzymes are embedded in the cell membrane.
The structure and function of membranes
Factors affecting membrane structure
Diffusion
Active Transport
Osmosis
, The Structure and Function of Membranes
All biological membranes are composed mainly of lipid and protein molecules.
The three major types of lipids in cell membranes are:
- Phospholipids, which are the most abundant.
- Cholesterol, which is responsible for stabilising the membrane.
- Glycolipids, which are found at the external surface of the membrane.
The proteins within the membrane are largely concerned with the transport of molecules
across the membrane.
When phospholipid molecules are surrounded by a watery environment on all sides, they
group together to bury their hydrophobic tails while leaving their hydrophilic heads exposed
to water. They form a bilayer with the fatty acid chains positioned towards the non-aqueous
interior and the polar heads in contact with water. The lipid bilayer is, however, relatively
impermeable to many important molecules.
The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure
The fluid mosaic model describes
the double layer of phospholipids
with proteins penetrating this
layer. The proteins are globular
and form a mosaic in the fluid-like
lipid bilayer.
Glycoproteins and glycolipids form
part of the external structure of
the membrane.
Cholesterol molecules are positioned within the bilayer close to the fatty acid chains; these
molecules partially immobilise these chains and help to stabilise the membrane.
Extrinsic proteins:
- On surface or partially embedded.
- Give mechanical support and act as cell recognition sites/receptors.
- Sometimes called ‘Peripheral membrane proteins’
Intrinsic proteins:
- Completely span the bilayer.
- They are water filled tubes that allow water solube ions to diffuse across.
- Carrier proteins bind to ions or water-soluble molecules like glucose and amino acids and
then change shape in order to move these proteins across the membrane.
- Enzymes are embedded in the cell membrane.