6th lecture - Van den Brand – How to obtain a good quality chicken?
What happens with an egg/embryo?
▪ Ovulation: follicles on the ovary that are ovulating
▪ Fertilization in the oviduct (infundibulum)
-Then the fertilized yolk travels from the oviduct (for 24 hours) and the egg is taking position
▪ Oviposition (ωοτοκία)
▪ Storage of eggs at the breeder farm (for a certain amount of time 1-5 days)
▪ Transportation
▪ Storage of eggs at the hatchery
-if it takes up to 2 wks then it is called prolonged storage
▪ Incubation
-After 21 days
▪ Hatching
▪ Chicken handling
▪ Transport of chickens to farm
F1: the yolk that is going to ovulate first.
The sperms travel through the cloaca to
the yolks -> fertilized ovum -> FO
travels to cloaca where all the positions
taking place.
The yolk is at the magnum for around
three hours, isthmus 1 hour.
Shell gland takes approx. 2 hours.
Video info:
Day 3: blood vessels on day 3
Eyes present on day 4 (extremely large at the beginning)
Day 8 fetal follicles (εμβρυϊκά ωοθυλάκια) are developing.
Day 10 tail end, first fetus occurring.
1
,Day 14 is completed but it only must grow, the yolk is outside the chicken (in comparison
with mammals)
Day 17 and after the yolk is incorporating in the belly of the chicken.
Day 15 The head is still between the legs.
Day 14-19 the yolk is still present.
Day 19 the yolk is gone (it is still present in the chicken)
Day 20-21 the hatching has started.
Photo of chicken Day 0: the down to dry (feathers) takes approx. 3 hours.
What is a good quality chicken?
▪ Chicken that shows a good performance
• Livability
• No/Low use of medicines.
• Able to cope with (pathogenic) challenges.
• Eggs
• (Breast) meat yield
• High efficiency ➔ low environmental pollution
▪ Chicken that has good health and welfare
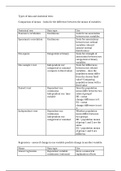
How to determine quality of a chicken? (3 different ways below)
▪ Physical quality
o Visual score
- Tona / Pasgar score
o Body weight
o Yolk free body mass
o Chicken length
▪ Immunological quality (Aart Lammers)
▪ Microbiological quality (not discussed)
2
,->Visual score-photo: eyes open-
bright-clean,(color is not important
for visual score), posture, navel
(ομφαλός) must be closed in order
to prevent pathogens from entering,
beak (ράμφος), legs (straight)-red
hocks and shoulders means that
the hatching progress was difficult
and that is not what we want,
behavior (the ability to raise
themselves immediately if we lean
them on their back of their head).
+ Fast method / General overview
- Subjective (υποκειμενικό)
->Body Weight: if egg weights 67g, yolk 20g
and the chicken has 2.5g means that 70%
used, this means that the chicken with less
yolk is more developed, so the residential
yolk the better.
+ Easy / Objective
- Unknown amount residual yolk
->Yolk free body mass: for science it can be
done, but not for practice, because you
have to kill your chickens to get
measurements.
+ Indicator chicken development &
performance
- Sacrifice chickens
Chicken body mass – yolk mass = yolk free body mass
->Chicken length: indicates chicks’ development and performance. Mostly for research,
almost every time, the bigger the better.
3
, Option C is a no
because you must
kill the chicken.
For option B
• Egg white: 50-
55g
• Breeders of
60 wks. old eggs
weight 75g -> 55g
of chick weight
• Relationship
between egg
weight and
chicken weight in
all bird species is
70% (65-75%) ->
35g of chick
weight.
So, you have to combine option B with option A.
Option D: Quite subjective do not do it
4
What happens with an egg/embryo?
▪ Ovulation: follicles on the ovary that are ovulating
▪ Fertilization in the oviduct (infundibulum)
-Then the fertilized yolk travels from the oviduct (for 24 hours) and the egg is taking position
▪ Oviposition (ωοτοκία)
▪ Storage of eggs at the breeder farm (for a certain amount of time 1-5 days)
▪ Transportation
▪ Storage of eggs at the hatchery
-if it takes up to 2 wks then it is called prolonged storage
▪ Incubation
-After 21 days
▪ Hatching
▪ Chicken handling
▪ Transport of chickens to farm
F1: the yolk that is going to ovulate first.
The sperms travel through the cloaca to
the yolks -> fertilized ovum -> FO
travels to cloaca where all the positions
taking place.
The yolk is at the magnum for around
three hours, isthmus 1 hour.
Shell gland takes approx. 2 hours.
Video info:
Day 3: blood vessels on day 3
Eyes present on day 4 (extremely large at the beginning)
Day 8 fetal follicles (εμβρυϊκά ωοθυλάκια) are developing.
Day 10 tail end, first fetus occurring.
1
,Day 14 is completed but it only must grow, the yolk is outside the chicken (in comparison
with mammals)
Day 17 and after the yolk is incorporating in the belly of the chicken.
Day 15 The head is still between the legs.
Day 14-19 the yolk is still present.
Day 19 the yolk is gone (it is still present in the chicken)
Day 20-21 the hatching has started.
Photo of chicken Day 0: the down to dry (feathers) takes approx. 3 hours.
What is a good quality chicken?
▪ Chicken that shows a good performance
• Livability
• No/Low use of medicines.
• Able to cope with (pathogenic) challenges.
• Eggs
• (Breast) meat yield
• High efficiency ➔ low environmental pollution
▪ Chicken that has good health and welfare
How to determine quality of a chicken? (3 different ways below)
▪ Physical quality
o Visual score
- Tona / Pasgar score
o Body weight
o Yolk free body mass
o Chicken length
▪ Immunological quality (Aart Lammers)
▪ Microbiological quality (not discussed)
2
,->Visual score-photo: eyes open-
bright-clean,(color is not important
for visual score), posture, navel
(ομφαλός) must be closed in order
to prevent pathogens from entering,
beak (ράμφος), legs (straight)-red
hocks and shoulders means that
the hatching progress was difficult
and that is not what we want,
behavior (the ability to raise
themselves immediately if we lean
them on their back of their head).
+ Fast method / General overview
- Subjective (υποκειμενικό)
->Body Weight: if egg weights 67g, yolk 20g
and the chicken has 2.5g means that 70%
used, this means that the chicken with less
yolk is more developed, so the residential
yolk the better.
+ Easy / Objective
- Unknown amount residual yolk
->Yolk free body mass: for science it can be
done, but not for practice, because you
have to kill your chickens to get
measurements.
+ Indicator chicken development &
performance
- Sacrifice chickens
Chicken body mass – yolk mass = yolk free body mass
->Chicken length: indicates chicks’ development and performance. Mostly for research,
almost every time, the bigger the better.
3
, Option C is a no
because you must
kill the chicken.
For option B
• Egg white: 50-
55g
• Breeders of
60 wks. old eggs
weight 75g -> 55g
of chick weight
• Relationship
between egg
weight and
chicken weight in
all bird species is
70% (65-75%) ->
35g of chick
weight.
So, you have to combine option B with option A.
Option D: Quite subjective do not do it
4