Mathematics Geometry Theory Questions with Verified Answers | Guaranteed Success
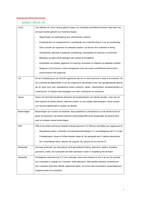
Acute Angle an angle that measures less than 90 degrees
Reflex Angle An angle greater than 180 degrees (but less than 360)
Obtuse Angle An angle that measures more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees
Revolution Angle (Angles around a point) An angle that is exactly 360 degrees
Straight Angle (Straight Line) An angle that measures 180 degrees
Right Angle An angle that measures 90 degrees
Complementary Angle Two angles that add up to 90 degrees
Supplementary Angle Two angles that add up to 180 degrees
Vertically Opposite Angles Vertically opposite angles are equal
Parrallel Lines lines that never intersect
Corresponding Angles the angles that occupy the same relative position at each intersection
where a straight line crosses two others. If the two lines are parallel, the corresponding angles
are equal. (Think of the 'F' rule.)
Alternate Angles angles on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the parallel lines
(think of the "Z" rule) are equal in size.
Acute Angle an angle that measures less than 90 degrees
Reflex Angle An angle greater than 180 degrees (but less than 360)
Obtuse Angle An angle that measures more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees
Revolution Angle (Angles around a point) An angle that is exactly 360 degrees
Straight Angle (Straight Line) An angle that measures 180 degrees
Right Angle An angle that measures 90 degrees
Complementary Angle Two angles that add up to 90 degrees
Supplementary Angle Two angles that add up to 180 degrees
Vertically Opposite Angles Vertically opposite angles are equal
Parrallel Lines lines that never intersect
Corresponding Angles the angles that occupy the same relative position at each intersection
where a straight line crosses two others. If the two lines are parallel, the corresponding angles
are equal. (Think of the 'F' rule.)
Alternate Angles angles on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the parallel lines
(think of the "Z" rule) are equal in size.