StraighterLine Microbiology BIO250
Comprehensive Final Exam Review | 2026
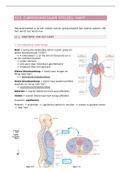
1. Where does translation occur? - ANSWER The cytoplasm
2. What develops as a complication of strep throat? - ANSWER Rheumatic
fever
3. IgG - ANSWER Previous exposure
Can cross the placenta
Monomer
Longer lasting immunity
4. IgA - ANSWER Dimer
Secretions (saliva, tears)
Most abundant
5. IgM - ANSWER Pentomer
Held together by "J-chain"
1st antibody to react
Largest
Current infection
6. IgD - ANSWER Monomer
Found on surface of B-cells
Helps immediate immune response
7. IgE - ANSWER Monomer
On Basophils
Allergic reactions & Parasitic worms
8. Rank the WBC's from most to least abundant - ANSWER Neutrophil
Lymphocyte
Monocyte
Eosinophil
Basophil
, 2
Neutrophil - ANSWER Phagocytic
Lymphocyte - ANSWER Specific immunity T-cells, B-cells & natural killer
cells
Monocyte - ANSWER Phagocytic as mature macrophages
Eosinophil - ANSWER Toxic to parasites
Basophils - ANSWER Produce histamines to combat allergic reactions
9. What are chemoheterotrophs? - ANSWER Organisms that get carbon from
organic material such as proteins, carbohydrates & lipids
10.What are chemoautotrophs & photoautotrophs? - ANSWER They get their
carbon from carbon dioxide
11.Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes use aerobic respiration as a way to produce
ATP, but you get the (most/least) ATP from aerobic respiration in
prokaryotes - ANSWER Most
12.What is the final electron acceptor? - ANSWER Oxygen
13.What is a Transforming Infection? - ANSWER Virus that alters cell DNA,
leading to cancer
14.What is a lysogenic infection? - ANSWER Phage DNA is incorporated into
host genome and is passed on to subsequent generations
15.What is a Lytic Bacteriophage Infection? - ANSWER Host cell gets so
packed with viruses that is lyses (splits) open and releases mature virions
16.What are the three principle purposes of cultivating viruses? - ANSWER 1.)
Isolate and ID viruses in clinical specimens
2.) Prepare viruses for vaccines
3.) Research viral strucutre, multiplication cycles, genetics, and effects on
hosts
17.What are three ways in which viruses are cultivated? - ANSWER 1.) Using
live animal inoculation
, 3
2.) Using bird embryos
3.) Using cell (tissue) culture techniques
18.What are three noncellular infections agents besides viruses? - ANSWER
Prions, viroids, and satellite viruses.
19.List the essential nutrients of a bacterial cell: - ANSWER CHONPS
C - arbon
H - ydrogen
N - itrogen
P - hosphate
S - ulphur
20.What are four terms that describe an organisms source of Carbon and
Energy? - ANSWER Photoautotrophos, chemoautotrophs,
chemoheterotrophs, lithoautotrophs
21.Define Saprobe: - ANSWER A microbe that decomposes organic remains
from dead organisms
22.Define Parasite - ANSWER An organism that lives in or within a host from
which it obtains nutrients and enjoys protection. Produces some degree of
harm to host
23.Define Diffusion: - ANSWER movement from high to low
24.Define Osmosis: - ANSWER Diffusion of water through a selectively
permeable membrane
25.hypotonic cell: - ANSWER cells that are less concentrated than their
environment; water rushes in, may burst cell
26.hypertonic cell: - ANSWER cells that are more concentrated than their
environment; water rushes out of the cell causing it to shrivel
27.isotonic cell: - ANSWER extracellular environment has the same
concentration of solutes as the cell cytoplasm
28.types of passive transport - ANSWER Facilitated diffusion, molecule-
specific, simple diffusion
, 4
29.facilitated diffusion - ANSWER passive transport: Movement of specific
molecules across cell membranes through protein channels by binding to
receptors
30.Molecule specific
transport - ANSWER Passive transport goes both directions. Rate is limited
by number of binding sites on transport proteins
31.Simple diffusion - ANSWER Fundamental property of atoms and molecults
that exist in a state of random motion
32.Name three types of active transport: - ANSWER Carrier mediated, group
translocation, bulk transport
33.Carrier-mediated Transport is... - ANSWER Active transport where atoms or
molecules are pumped into or out of the cell by specialized receptors
34.Group translocation transport is.... - ANSWER Active transport where
molecule is moved across membrane and converted to a metabolically useful
substance
35.Bulk transport is.... - ANSWER active transport of large
particles/cells/liquids by enfulcing in a vesicle (e.g. endocytosis,
phagocytosis, etc.)
36.Ways in which different organisms dead with oxygen... - ANSWER Can use
oxygen and detoxify is, can neither use nor detoxify is, cannot use but can
detoxify it.
37.What are the five types of associations microbes can have with their hosts? -
ANSWER Mutualism, Commensalism, Parasitism, Antagonism, Synergism
38.Define mutualism - ANSWER both organisms benefit
39.Define commensalism - ANSWER one species benefits and the other is
neither harmed nor helped
40.Define Parasitism - ANSWER one species benefits (parasite) and the other is
harmed (host)