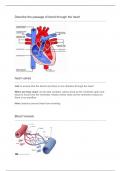
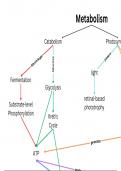
- Two main types of hazards HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL and GEOPHYSICAL
Hydro meteorological (caused by climatic processes) Geophysical (caused by physical processes)
Tropical storm Tectonic Geomorphological
Tornadoes Volcanic eruptions, Landslides
Wild fires Earthquakes Avalanches
Drought Tsunamis
Floods
Sandstorms
- Disasters result when hydro-meteorological and geophysical hazards threaten the life & property of
increasing no‟s of the world‟s people.
- The Risk of disaster grows as global Hazards and people‟s Vulnerability increases, while their
Capacity to cope decreases.
Disaster – a hazard becoming a reality in an event that causes death and damage to goods and property
and the environment.
Risk – The probability of a hazard event occurring and causing loss of life or injury, property damage etc.
Vulnerability – How susceptible a population is to the damage caused by a hazard.
The …DISASTER Disaster Risk [D] = Freq./magnitude of Hazards [H] x Vulnerability [V]
RISK EQUATION Capacity to Cope [C]
- Equation measures the level of Hazard for an area
- Degg’s Model how a hazard becomes a disaster
, Why do people live in risk areas?
- Some people may not know that they live in a hazardous area, but others may consistently place
themselves at risk from natural hazards. Why?
- Lack of alternatives
- Unpredictability
- Changing dangers
- Cost vs. Benefit
Frequency or Magnitude of Hazard
- This is unfortunately increasing
- Mainly due to use of fossil fuels increasing the frequency and severity of weather
Level of Vulnerability
- This is increasing
- Hazards only become hazards when people get in the way the world‟s pop. Increasing rapidly so
more people are having to live in hazard prone areas.
Capacity to Cope
- This is decreasing
- Communities need the skills, tools and money to cope with the effects of climate change
- Debt repayments
- Unfair trade arrangements
- MEDCs directing aid funds towards politically strategic regions rather than those meet in need
WHY THE POOREST AREAS LACK THE MONEY NEEDED
, - Tropical island
- 100,000 people (pop. In 2011)
- Officially the republic of Kiribati
- Formerly owned by UK
- Located in the middle of the Pacific Ocean
- Neighbours: Fiji, Australia, New Zealand, Indonesia
- One impact: rising sea levels e.g. island of Tebua under sea
Why are sea levels rising?
- Land-based glaciers melting contributes to sea level (not sea-based glaciers)
due to global warming
- Thermal expansion of water due to global warming
What is happening to the people of Kiribati?
- Environmental refugee = person forced to migrate as a result of changes to their environment.
- People from Kiribati are becoming some of the world‟s first environmental refugees
Where will the people of Kiribati go?
“Australia and New Zealand should accept all environmental refugees from Kiribati”
- The New Zealand and Australian government may not be able to cope New Zealand already
accepted refugees from Tuvalu