Pedorthics Exam 1 | comprehensive Q&A for
certification success
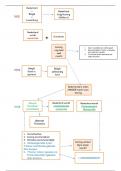
Rearfoot (Tarsus), Midfoot (Lesser tarsus), and Forefoot (Metatarsus) -correct-
answer-Functional components of the foot
Which bones make up the rearfoot? -correct-answer-Calcaneus and talus
Which bones make up the midfoot? -correct-answer-Navicular and cuboid
Which bones make up the forefoot? -correct-answer-Cuneiforms 1-3 and digits
Medial column of the foot -correct-answer-70% of the load. More flexible.
Composed of the talus, navicular, cuneiforms, and metatarsals 1-3
Lateral column of the foot -correct-answer-30% of the load. More rigid.
Composed of the calcaneus, cuboid, and metatarsals 4-5
,2|Page
Calcaneus -correct-answer-Largest bone in the foot, insertion point for the
achilles, articulates with talus and cuboid
Orthotic intervention for metatarsalgia -correct-answer-sulcus to full length
orthoses, reduce shear forces, met pad/bar,
Metatarsal pad -correct-answer-Shaped like distorted guitar pick. Used to relieve
pressure/callusing under metatarsals 2-4
Morton's toe -correct-answer-Shortened 1st Metatarsal in Relation to 2nd
Metatarsal. Increased Pressure Under 2nd/3rdMetatarsals
Biomechanical Reason for This: Pressure not taken on the first ray in terminal
stance
Orthotic intervention for morton's toe -correct-answer-Full Length Orthosis
Morton's Extension
Metatarsal Pad
, 3|Page
Morton's neuroma -correct-answer-Thickening of plantar nerve between 3rd/4th
met heads. Also can occur between 2nd/3rdMets.
Orthotic intervention for morton's neuroma -correct-answer-Full Length Orthosis
and Metatarsal Pad
Turf toe -correct-answer-Hyperextension of the 1st MTP joint
Orthotic intervention for turf toe -correct-answer-Full Length Orthosis and
Morton's Extension
Orthotic intervention for plantar fasciitis -correct-answer-Rigid FO, Pre-Met (3/4)
to Full Length Orthosis to limit windlass affect, Control Hyper-pronation with
Posting, provide MLA, heel pad
Temporary orthotic intervention for plantar fasciitis -correct-answer-Heel
elevation to relieve tension on plantar fascia. If prolonged, it will worsen condition