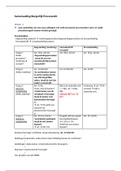
TOPIC 1
Law → set of principles and norms (based on an idea of justice and order) that regulate
human relations and represent consequences that can be enforced by authority.
Important distinction →
● Values: beliefs considered right (freedom, justice, equality)
● Principles: framework for decision-making and behavior, deriving from values
● Norms: social rules and expectations (related to law)
Definitions →
● Enforceability: claiming before a judge the fulfillment of a law/regulation
● Legal certainty: predictability of the legal consequences of acts or conduct
Ordinary jurisdiction →
● Criminal: basically just crimes (theft, murder, assault)
● Contentious-administrative: citizens vs public authorities (taxes, immigration)
● Social: social welfare and protection (adoption, divorce)
● Civil: the rest of conflicts (contracts, property rights)
Laws in each department →
● New product /service idea (Intellectual and Industrial Property Law)
● Financing (Contract Law, Tax Law)
● Incorporation (Company Law)
● Employees (Labor Law, Personal Data Protection Law, Tax Law)
● Collaborators (Contract Law)
● Marketing (Competition Law, Patent and Trademark Law)
● Accounting (Accounting Law, Commercial Law, Company Law, Tax Law)
● Website and e-commerce (Personal Data Protection Law, E-Commerce Law)
Legal tools of intermediation with stakeholders →
(individual or organization that is impacted by the actions of a company)
● Owners: shareholder agreements, corporate governance policies
● Managers: employment contracts, executive compensation agreements
● Employees: employment contracts, workplace safety regulations
● Customers: contracts, warranties, consumer protection laws, privacy regulations
● Shareholders: agreements, proxy voting mechanisms, disclosure requirements
● Suppliers: contracts, procurement agreements, supply chain transparency
● Government: regulatory compliance, permits, licenses
● Society: corporate social responsibility
Lifecycle of a company →
● Start-up stage: market research, product development, legal structure
● Financing: seeking of funding
● Protection of key assets: trademarks, patents, copyrights, confidentiality agreements
● Going public (IPO): shares offered to the public to be traded on stock exchange
● Corporate reorganizations: adapting to the market, forming strategic initiatives
● Dissolution: liquidating assets, paying off creditors, distributing assets
Law → set of principles and norms (based on an idea of justice and order) that regulate
human relations and represent consequences that can be enforced by authority.
Important distinction →
● Values: beliefs considered right (freedom, justice, equality)
● Principles: framework for decision-making and behavior, deriving from values
● Norms: social rules and expectations (related to law)
Definitions →
● Enforceability: claiming before a judge the fulfillment of a law/regulation
● Legal certainty: predictability of the legal consequences of acts or conduct
Ordinary jurisdiction →
● Criminal: basically just crimes (theft, murder, assault)
● Contentious-administrative: citizens vs public authorities (taxes, immigration)
● Social: social welfare and protection (adoption, divorce)
● Civil: the rest of conflicts (contracts, property rights)
Laws in each department →
● New product /service idea (Intellectual and Industrial Property Law)
● Financing (Contract Law, Tax Law)
● Incorporation (Company Law)
● Employees (Labor Law, Personal Data Protection Law, Tax Law)
● Collaborators (Contract Law)
● Marketing (Competition Law, Patent and Trademark Law)
● Accounting (Accounting Law, Commercial Law, Company Law, Tax Law)
● Website and e-commerce (Personal Data Protection Law, E-Commerce Law)
Legal tools of intermediation with stakeholders →
(individual or organization that is impacted by the actions of a company)
● Owners: shareholder agreements, corporate governance policies
● Managers: employment contracts, executive compensation agreements
● Employees: employment contracts, workplace safety regulations
● Customers: contracts, warranties, consumer protection laws, privacy regulations
● Shareholders: agreements, proxy voting mechanisms, disclosure requirements
● Suppliers: contracts, procurement agreements, supply chain transparency
● Government: regulatory compliance, permits, licenses
● Society: corporate social responsibility
Lifecycle of a company →
● Start-up stage: market research, product development, legal structure
● Financing: seeking of funding
● Protection of key assets: trademarks, patents, copyrights, confidentiality agreements
● Going public (IPO): shares offered to the public to be traded on stock exchange
● Corporate reorganizations: adapting to the market, forming strategic initiatives
● Dissolution: liquidating assets, paying off creditors, distributing assets