Lewis acid: a substance which accepts a pair When an ionic solid dissolves in a solu
of electrons from another substance. Solubility-product constant, Ksp: the
Lewis base: a substance which donates a pair equilibrium constant for the equilibri
of electrons to another substance. between an ionic solid solute and its
Metal ions which accept electron pairs are saturated aqueous solution.
often simply referred to as inorganic acids. For the equilibrium: aA(s) bB(aq) + cC
It would be fair to say that almost all metals Ksp = [B]^b[C]^c
in aqueous solutions behave as acids
Heterogeneous Equilibrium:
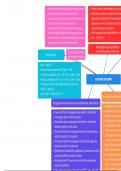
Lewis acids, bases Solubility product and Ksp
The pH scale
and inorganic acids
pH = -log[H+]
In neutral solutions at 25°C, pH = 7.00.
In acidic solutions, [H+] > 1.0 × 10–⁷, so pH < 7.00.
In basic solutions, [H+] < 1.0 × 10–⁷, so pH > 7.00. ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA
The lower the pH, the more acidic the solution.
pOH = -log[OH–]
pH + pOH = 14.00 (at 25 °C)
Strength of acids and b
Conjugate acid-base pairs and amphoteric substances
Strong acid: an acid
Every acid has a conjugate base which is formed by Monoprotic acid: an
removing a proton from the acid. Polyprotic acids: aci
Every base has a conjugate acid which is formed by Strong base: a base
adding a proton to the base. Weak bases: bases w
The more stable the conjugate base, the stronger the will be a mixture of i
acid from which it is derived. - Neutral substances
The more stable the conjugate acid, the stronger the - Anions of weak acid
base from which it is derived. Weak acids: acids th
Amphoteric/amphiprotic substance: A substance which results in a mixture o
can act as either an acid or a base In a strong acid-stro
Autoionization: The process in which like molecules each other by reacti
react to yield ions acid or the base will
Ka is called the acid
of electrons from another substance. Solubility-product constant, Ksp: the
Lewis base: a substance which donates a pair equilibrium constant for the equilibri
of electrons to another substance. between an ionic solid solute and its
Metal ions which accept electron pairs are saturated aqueous solution.
often simply referred to as inorganic acids. For the equilibrium: aA(s) bB(aq) + cC
It would be fair to say that almost all metals Ksp = [B]^b[C]^c
in aqueous solutions behave as acids
Heterogeneous Equilibrium:
Lewis acids, bases Solubility product and Ksp
The pH scale
and inorganic acids
pH = -log[H+]
In neutral solutions at 25°C, pH = 7.00.
In acidic solutions, [H+] > 1.0 × 10–⁷, so pH < 7.00.
In basic solutions, [H+] < 1.0 × 10–⁷, so pH > 7.00. ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA
The lower the pH, the more acidic the solution.
pOH = -log[OH–]
pH + pOH = 14.00 (at 25 °C)
Strength of acids and b
Conjugate acid-base pairs and amphoteric substances
Strong acid: an acid
Every acid has a conjugate base which is formed by Monoprotic acid: an
removing a proton from the acid. Polyprotic acids: aci
Every base has a conjugate acid which is formed by Strong base: a base
adding a proton to the base. Weak bases: bases w
The more stable the conjugate base, the stronger the will be a mixture of i
acid from which it is derived. - Neutral substances
The more stable the conjugate acid, the stronger the - Anions of weak acid
base from which it is derived. Weak acids: acids th
Amphoteric/amphiprotic substance: A substance which results in a mixture o
can act as either an acid or a base In a strong acid-stro
Autoionization: The process in which like molecules each other by reacti
react to yield ions acid or the base will
Ka is called the acid