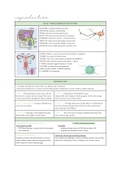
MALE + FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
BLADDER: storage & emptying of urine
PROSTATE: produces seminal fluid
PENIS: urination and sexual intercourse
HEAD: where pee, precum and cum are released
FORESKIN: protective, sensory + sexual functions
TESTICLE: make sperm and produce testosterone
URETHRA: connects urinary bladder to the penis
S.VESICLE: move s.fluid and sperm → urethra → out
OVARY: produce + store ovum, and contoles period + pregnancy
UTERUS: to accept a fertilized ovum
VAGINA: role in sex, menstruation, pregnancy & childbirth
CERVIX: allows fluid to pass between uterus + vagina
F. TUBE: transports eggs from ovary → uterus
CLITORIS: to experience sexual pleasure
LABIA: protect vaginal + urethral openings
U. OPENING: for urinating
MENSTRUATION
- A woman’s reproductive system works on a 28 day cycle= menstrual
- menstrual cycle function is to ensure that the female body is prepared to conceive a baby at regular intervals.
1) DAY 1-7 The menstruation cycle starts with the 2) DAY 8-13 Around day 7 the blood flow stops.
first day of a woman’s period. Lining of the uterus Lining of the uterus begins to build up again. At this time an egg
comes away and exits through the vagina as blood. starts to mature in one of the ovaries.
3) DAY 14 (THE MIDDLE) An egg is released by an 4) DAY 14 - 17 The egg can last up to 3 days after it is released from
ovary into the oviduct. the ovary. During, the egg travels down the oviduct and into the
uterus hoping to be fertilized.
5) DAY 18 - 28 If the egg is not fertilised then the 6) DAY 1 – 7 The cycle starts over again expelling the lining of the
lining of the uterus begins to break down. uterus and the egg = period.
4 HORMONES IN MENSTRUAL CYCLE *= follicle stimulating hormone
PITUITARY GLAND OVARIES
- FSH* (develops egg + causes release of oestrogen) - oestrogen (stops release of FSH and produces LH)
- LH (ovulation) - progesterone (mantains uterus’ lining)
CONTROLLING FERTILITY Taking the pill can lead to health problems.
Scientists can use artificial hormones to control Gain weight, get headaches or feel sick. Blood pressure can increase,
fertility. Many women take the contraceptive pill, blood clots can develop. There is a higher risk of breast cancer.
which stops the ovaries releasing eggs.
, PREGNANCY - FETUS DEVELOPMENT
FIRST TRIMESTER
30 HOURS AFTER FERTILISATION- A zygote has only just been through fertilisation and has divided once.
FIRST 2 WEEKS- OVULATION (egg released from ovary)
2 WEEKS AFTER (END)- FERTILISATION (genetic material mom dad combine- characteristics)
3 WEEKS AFTER- blastocyst arrange themselves in 2 groups (inner= baby, outer= protect)
5 WEEKS AFTER- It is now the size of a raisin. The brain and spinal cord are starting to develop.
6 WEEKS AFTER- A heart has started to beat. Arms and legs start to form.
8 WEEKS AFTER- It is now called a fetus. It is producing its own stomach digestive juices.
9 WEEKS AFTER- Fingerprints are now formed and it will grip objects placed in its hand.
10 WEEKS AFTER (END)- fetus
14 WEEKS- Muscles form and the baby starts to move. Eyelids, fingernails, toenails form.
18 WEEKS- About 5 inches long. It can blink and grasp. Hair grows all over the body.
24 WEEKS- Fine hair and a waxy substance covers the body. It starts to ‘breathe’.
30 WEEKS- The baby can survive if born now. It would be called premature.
40 WEEKS- A normal baby is born around this time.
PLACENTA
- the placenta contains the amniotic fluid, and also is where the umbilical cord is attached
- AMN. FLUID: Protective liquid in Amniotic sac (is an efficient shock absorber to protect Fetus from impact, creates
buoyancy to ensure Fetus does not have to support own weight while Skeletal system develops)
- Materials including Oxygen, Nutrients, Vitamins, Antibodies and Water diffuse across Placenta from Mother to Fetus
PUBERTY- HORMONES
- Hormones are chemical messengers that travel around the body.
- The end. system (organs and glands) coordinates changes in the body using hormones.
- A gland secretes a hormone into the blood, it travels in the bloodstream until it reaches
its target organ.
- The advantage of hormonal coordination is it can have a more long lasting effect.
- The disadvantage is that it takes longer to work.
- A good example of this is puberty. Sex hormones (oestrogen and testosterone) are
released from the sexual organs and cause the changes to the body over a number of years.
END. SYSTEM: coordinating the reproductive system. During puberty testosterone is made in the testes in high levels
(causes males to develop the secondary sex characteristics of body hair, deeper voice, sperm production…). The ovaries
secrete oestrogen (causes females to develop breasts, grow body hair, widen their hips and they begin to ovulate).
growth of the pollen tube followed by fertilization leads to seed and fruit formation
- Pollination involves the transfer of Pollen grain from an Anther (male structure) to a Stigma (female structure)
- Pollen grain lands on Stigma, then a Pollen tube grows down the Style until reaches an Ovule in the Ovary
- Allows the N of Pollen grain to pass along the Pollen tube to fuse with Nucleus of Ovule (via fertilization)
- = Ovule form a Seed, Ovule wall forms Seed coat, the rest of Carpel will develop into a Fruit to carry the Seed
germinating seeds use food reserves stored in the seed until the seedling is big to carry out photosynthesis
BLADDER: storage & emptying of urine
PROSTATE: produces seminal fluid
PENIS: urination and sexual intercourse
HEAD: where pee, precum and cum are released
FORESKIN: protective, sensory + sexual functions
TESTICLE: make sperm and produce testosterone
URETHRA: connects urinary bladder to the penis
S.VESICLE: move s.fluid and sperm → urethra → out
OVARY: produce + store ovum, and contoles period + pregnancy
UTERUS: to accept a fertilized ovum
VAGINA: role in sex, menstruation, pregnancy & childbirth
CERVIX: allows fluid to pass between uterus + vagina
F. TUBE: transports eggs from ovary → uterus
CLITORIS: to experience sexual pleasure
LABIA: protect vaginal + urethral openings
U. OPENING: for urinating
MENSTRUATION
- A woman’s reproductive system works on a 28 day cycle= menstrual
- menstrual cycle function is to ensure that the female body is prepared to conceive a baby at regular intervals.
1) DAY 1-7 The menstruation cycle starts with the 2) DAY 8-13 Around day 7 the blood flow stops.
first day of a woman’s period. Lining of the uterus Lining of the uterus begins to build up again. At this time an egg
comes away and exits through the vagina as blood. starts to mature in one of the ovaries.
3) DAY 14 (THE MIDDLE) An egg is released by an 4) DAY 14 - 17 The egg can last up to 3 days after it is released from
ovary into the oviduct. the ovary. During, the egg travels down the oviduct and into the
uterus hoping to be fertilized.
5) DAY 18 - 28 If the egg is not fertilised then the 6) DAY 1 – 7 The cycle starts over again expelling the lining of the
lining of the uterus begins to break down. uterus and the egg = period.
4 HORMONES IN MENSTRUAL CYCLE *= follicle stimulating hormone
PITUITARY GLAND OVARIES
- FSH* (develops egg + causes release of oestrogen) - oestrogen (stops release of FSH and produces LH)
- LH (ovulation) - progesterone (mantains uterus’ lining)
CONTROLLING FERTILITY Taking the pill can lead to health problems.
Scientists can use artificial hormones to control Gain weight, get headaches or feel sick. Blood pressure can increase,
fertility. Many women take the contraceptive pill, blood clots can develop. There is a higher risk of breast cancer.
which stops the ovaries releasing eggs.
, PREGNANCY - FETUS DEVELOPMENT
FIRST TRIMESTER
30 HOURS AFTER FERTILISATION- A zygote has only just been through fertilisation and has divided once.
FIRST 2 WEEKS- OVULATION (egg released from ovary)
2 WEEKS AFTER (END)- FERTILISATION (genetic material mom dad combine- characteristics)
3 WEEKS AFTER- blastocyst arrange themselves in 2 groups (inner= baby, outer= protect)
5 WEEKS AFTER- It is now the size of a raisin. The brain and spinal cord are starting to develop.
6 WEEKS AFTER- A heart has started to beat. Arms and legs start to form.
8 WEEKS AFTER- It is now called a fetus. It is producing its own stomach digestive juices.
9 WEEKS AFTER- Fingerprints are now formed and it will grip objects placed in its hand.
10 WEEKS AFTER (END)- fetus
14 WEEKS- Muscles form and the baby starts to move. Eyelids, fingernails, toenails form.
18 WEEKS- About 5 inches long. It can blink and grasp. Hair grows all over the body.
24 WEEKS- Fine hair and a waxy substance covers the body. It starts to ‘breathe’.
30 WEEKS- The baby can survive if born now. It would be called premature.
40 WEEKS- A normal baby is born around this time.
PLACENTA
- the placenta contains the amniotic fluid, and also is where the umbilical cord is attached
- AMN. FLUID: Protective liquid in Amniotic sac (is an efficient shock absorber to protect Fetus from impact, creates
buoyancy to ensure Fetus does not have to support own weight while Skeletal system develops)
- Materials including Oxygen, Nutrients, Vitamins, Antibodies and Water diffuse across Placenta from Mother to Fetus
PUBERTY- HORMONES
- Hormones are chemical messengers that travel around the body.
- The end. system (organs and glands) coordinates changes in the body using hormones.
- A gland secretes a hormone into the blood, it travels in the bloodstream until it reaches
its target organ.
- The advantage of hormonal coordination is it can have a more long lasting effect.
- The disadvantage is that it takes longer to work.
- A good example of this is puberty. Sex hormones (oestrogen and testosterone) are
released from the sexual organs and cause the changes to the body over a number of years.
END. SYSTEM: coordinating the reproductive system. During puberty testosterone is made in the testes in high levels
(causes males to develop the secondary sex characteristics of body hair, deeper voice, sperm production…). The ovaries
secrete oestrogen (causes females to develop breasts, grow body hair, widen their hips and they begin to ovulate).
growth of the pollen tube followed by fertilization leads to seed and fruit formation
- Pollination involves the transfer of Pollen grain from an Anther (male structure) to a Stigma (female structure)
- Pollen grain lands on Stigma, then a Pollen tube grows down the Style until reaches an Ovule in the Ovary
- Allows the N of Pollen grain to pass along the Pollen tube to fuse with Nucleus of Ovule (via fertilization)
- = Ovule form a Seed, Ovule wall forms Seed coat, the rest of Carpel will develop into a Fruit to carry the Seed
germinating seeds use food reserves stored in the seed until the seedling is big to carry out photosynthesis