Photon - ‘packet of energy’
Electrons fill energy levels from the bottom up.
If you give an electron the right amount of energy, in the form of a light, heat, sound, electric
photon, it will absorb the energy and jump to the next level.
Other electrons will give off photons and fall to the lower energy level.
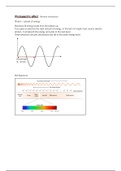
Wavelength
(ƛ - lamda)
EM Spectrum
, The wave equation for EM radiation
c=λxf
𝑐
λ=
𝑓
𝑐
f=
𝜆
c - “The speed of light”
The speed of electromagnetic radiation in a vacuum.
A constant = 3 x 108
Unit: m.s-1
λ - Lambda, representing wavelength
Unit: m
Note: Be aware of conversions
f - Frequency
Unit: Hz (s-1)
Note: Be aware of conversions
f is inversely proportional to λ
kilo = x 103
mega = x 106
giga = x 109
tera = x 1012
milli = x 10-3
micro = x 10-6
nano = x 10-9
pico = x 10-12
Example:
What is the wavelength of a microwave with a frequancy of 2.45 GHz?
c=λxf
3 x 108 = λ x (2.45 x 109)
λ = 0.122 m
Example:
What is the frequency of a TV wave with a wavelength of 240 m?
c=λxf
3 x 108 = (240) x f
f = 1 250 000 Hz