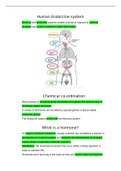
Human Endocrine system
- Nervous and endocrine systems enable animals to respond to external
changes and control conditions inside their bodies
Chemical co-ordination
- Slow process of communicating information throughout the body by way of
chemicals called hormones
- A variety of hormones are secreted by special glands or tissue called
endocrine glands
- The endocrine system works with the Nervous system
What is a hormone?
- An organic chemical substance, usually a protein but sometimes a steroid, is
secreted by an endocrine gland and carried in the bloodstream to its target
organs where it regulates metabolic reactions
- Metabolism: the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in
order to maintain life
- Hormones don’t last long in the body as they are broken down by enzymes
, What is a target organ?
- Although hormones are carried in the blood throughout the body, they can
only affect certain cells
- The specific cells that respond to a given hormone have receptor sites for that
hormone
- These cells are known as target organs
- They can be a single gland, organ or scattered throughout the body
What is an endocrine gland?
- A vascular, ductless gland that secretes hormones which are carried in the
bloodstream to their target organs
- Vascular: richly supplied with blood vessels
How do exo- and endocrine glands differ?
- The secretions of an exocrine gland are carried in ducts to where they are
needed
- Endocrine glands do not have ducts and their secretions are carried in the
bloodstream to their target organs
, 1.Hypothalamus
- The hypothalamus is part of the brain, situated above the pituitary gland
- It secretes the hormone ADH (anti-diuretic hormone)
What is the role of ADH?
- Osmoreceptors in the blood vessels of the hypothalamus detect an increase
in osmolarity (low water levels) of the blood
- The hypothalamus responds and releases ADH
- ADH helps to conserve water if the body is dehydrated
- It does this by causing more water to be reabsorbed back into the blood from
the collecting ducts of the kidney, so less water is lost in the urine
2. Pituitary gland
- This gland acts as the chemical co-ordinator of most of the other endocrine
glands and is therefore called the “master gland”
- It is attached to the hypothalamus at the base of the brain by a short stalk
What hormones are secreted by the pituitary?
1. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Stimulates thyroid gland to secrete thyroxin
2. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Females: stimulates oogenesis in the ovaries
Oogenesis: formation of eggs
Males: stimulates spermatogenesis in the testes
- Nervous and endocrine systems enable animals to respond to external
changes and control conditions inside their bodies
Chemical co-ordination
- Slow process of communicating information throughout the body by way of
chemicals called hormones
- A variety of hormones are secreted by special glands or tissue called
endocrine glands
- The endocrine system works with the Nervous system
What is a hormone?
- An organic chemical substance, usually a protein but sometimes a steroid, is
secreted by an endocrine gland and carried in the bloodstream to its target
organs where it regulates metabolic reactions
- Metabolism: the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in
order to maintain life
- Hormones don’t last long in the body as they are broken down by enzymes
, What is a target organ?
- Although hormones are carried in the blood throughout the body, they can
only affect certain cells
- The specific cells that respond to a given hormone have receptor sites for that
hormone
- These cells are known as target organs
- They can be a single gland, organ or scattered throughout the body
What is an endocrine gland?
- A vascular, ductless gland that secretes hormones which are carried in the
bloodstream to their target organs
- Vascular: richly supplied with blood vessels
How do exo- and endocrine glands differ?
- The secretions of an exocrine gland are carried in ducts to where they are
needed
- Endocrine glands do not have ducts and their secretions are carried in the
bloodstream to their target organs
, 1.Hypothalamus
- The hypothalamus is part of the brain, situated above the pituitary gland
- It secretes the hormone ADH (anti-diuretic hormone)
What is the role of ADH?
- Osmoreceptors in the blood vessels of the hypothalamus detect an increase
in osmolarity (low water levels) of the blood
- The hypothalamus responds and releases ADH
- ADH helps to conserve water if the body is dehydrated
- It does this by causing more water to be reabsorbed back into the blood from
the collecting ducts of the kidney, so less water is lost in the urine
2. Pituitary gland
- This gland acts as the chemical co-ordinator of most of the other endocrine
glands and is therefore called the “master gland”
- It is attached to the hypothalamus at the base of the brain by a short stalk
What hormones are secreted by the pituitary?
1. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Stimulates thyroid gland to secrete thyroxin
2. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Females: stimulates oogenesis in the ovaries
Oogenesis: formation of eggs
Males: stimulates spermatogenesis in the testes