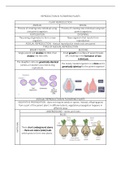
PLANT REPRODUCTION
ASEXUAL SEXUAL
Process of creating new individual using Process of creating new individual using two
one parent organism parent organisms
FERTILISATION OFFSPRING
The joining of gametes to form a new New organism that results from
organism reproduction
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION - Asexual reproduction needs only one parent
TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
BINARY FISSION BUDDING
Single parent cell doubles its DNA, then Small growth on surface of parent breaks
divides into two cells. off, resulting in the formation of two
individuals.
The daughter cells are genetically identical
the newly created organism is a clone and is
(unless a mutation occurred during
genetically identical to the parent organism
replication)
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
VEGATATIVE PROPAGATION - does not require seeds or spores. Instead, offspring grow
from a part of the parent plant. In different plants, vegetative propagation happens in
different ways
UNDERGROUND – stems and roots
BULBS
NATRURAL
These short underground stems
- there are lateral (side) buds
which grow to form new plants.
, TUBERS - root
These underground growths
produce new plants from stems
or growing points - eyes
swollen roots = root tubers
CORMS - root
similar to true bulbs BUT a corm
doesn’t have as many layers.
Corms are used up during the
growing season and get replaced
by one or more new corms.
NATRURAL
RHIZOMES - stem
These stems that grow sideways
along the soil or just below the
surface. They branch apart to
produce new points of growth. -
underground stem
ABOVE GROUND - stems
STOLON - RUNNER
plants produce long side shoots
that develop roots, eventually
forming a
new plant - branches growing
along the ground