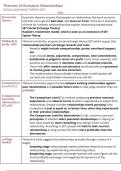
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Parts : -
Testes
-
Tubules (transport for sperm)
Accessory glands
-
-
Penis
,Testes "
2 =
testis
testes
Primary male Protects
→
sex
organ >
against physical injury
"
temp [34 -35 ]
"
suspended between legs regulates
'
→
in scrotum sac →
acts as a thermostat =
0
Optimal sperm production =
temp 2- 3°C lower than body temp .
*
Internally → testis ÷ into lobules →
each contain convoluted seminiferous tubules → lined with germinal epithelium .
*
Spermatogenesis (occurs in seminiferous tubules ) →
germinal epithelium
÷
(meiosis) =
sperm cells (male gametes)
Some epithelium develope into Sertoli cells ( long /columnar) provide food/nutrients for
cells developing cells
→
9
Semi tubules surrounded by connective tissue → contains interstitial cells
Leydig cells ( =
produces testosterone)
.
-
function
* produce i. release sperm
* Produces male sex hormone testosterone characteristics
: :
secondary
, Tubules
Epididymis (✗ 2)
seminiferous tubules join to form epididymis
→
→
situated at back of tester
>
lined with mucous membrane
functions
→ stores sperm where sperm matures
→
Mucous membrane =
secretes substance : moves sperm (with peristaltic movement)
Vas deferens sperm duct
Passes through abdominal opens into urethra
>
cavity +
just before urethra forms swelling ampulla
i. → =
a
Functions
→
Transports sperm =
peristaltic movement
Ejaculatory duct
Ampulla leads
ejaculatory duct
→
to
Function
→
Smooth muscle fibres in duct wall contract :
forcing semen along urethra
* Release of sperm =
ejaculation
Urethra
→ 2
ejaculatory ducts join urethra :
open to exterior
Function
→
Transports urine i. sperm
↳ never time !
pass @ same
Parts : -
Testes
-
Tubules (transport for sperm)
Accessory glands
-
-
Penis
,Testes "
2 =
testis
testes
Primary male Protects
→
sex
organ >
against physical injury
"
temp [34 -35 ]
"
suspended between legs regulates
'
→
in scrotum sac →
acts as a thermostat =
0
Optimal sperm production =
temp 2- 3°C lower than body temp .
*
Internally → testis ÷ into lobules →
each contain convoluted seminiferous tubules → lined with germinal epithelium .
*
Spermatogenesis (occurs in seminiferous tubules ) →
germinal epithelium
÷
(meiosis) =
sperm cells (male gametes)
Some epithelium develope into Sertoli cells ( long /columnar) provide food/nutrients for
cells developing cells
→
9
Semi tubules surrounded by connective tissue → contains interstitial cells
Leydig cells ( =
produces testosterone)
.
-
function
* produce i. release sperm
* Produces male sex hormone testosterone characteristics
: :
secondary
, Tubules
Epididymis (✗ 2)
seminiferous tubules join to form epididymis
→
→
situated at back of tester
>
lined with mucous membrane
functions
→ stores sperm where sperm matures
→
Mucous membrane =
secretes substance : moves sperm (with peristaltic movement)
Vas deferens sperm duct
Passes through abdominal opens into urethra
>
cavity +
just before urethra forms swelling ampulla
i. → =
a
Functions
→
Transports sperm =
peristaltic movement
Ejaculatory duct
Ampulla leads
ejaculatory duct
→
to
Function
→
Smooth muscle fibres in duct wall contract :
forcing semen along urethra
* Release of sperm =
ejaculation
Urethra
→ 2
ejaculatory ducts join urethra :
open to exterior
Function
→
Transports urine i. sperm
↳ never time !
pass @ same