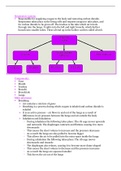
Reactions of metals and non-metals with oxygen
Reactions of metals with oxygen
Metal + oxygen metal oxide
Reactants products
Reaction of magnesium with oxygen
Forms the product magnesium oxide
2Mg + O2 2MgO
Produces a bright white light which can damage your eyes when burning. The end product
is a white powder
Reaction of iron with oxygen
A metal like iron will gradually react with oxygen in the atmosphere to form a metal oxide
e.g. iron oxide
Iron reacts easily with oxygen to form rust
Water and oxygen are required for iron to rust
2 types of iron oxide form:
• 4Fe + 3O2 2Fe2O3 = Rust
• 3Fe + 2O2 Fe3O4 = Magnetite
Rusting
Occurs on the surface of iron
Iron is in contact with oxygen and moisture/water
Rusting is a type of corrosion where metal is damaged or weakened
Reactive metals corrode quicker (group 1)
Non-reactive metals will not corrode even after many years (closer to zig-zag line on the
periodic table) such as gold or platinum
Preventing Rust
Galvanise
covering with another metal that does not rust so easily
Electroplating or chrome plating
process of electrolysis
deposits thin layer of chromium (more reactive metal)
forms shiny, attractive surfaces
Paint
prevents metal contact with water/moisture and oxygen
Bars that protect ships (sacrificial anodes)
connecting/adding more reactive metal bars (magnesium alloys or zinc)
bars corrode first
Oiling
oil repels water (oil is hydrophobic)
Reactions of non-metals with oxygen
Non-metal + oxygen non-metal oxide
Reactants product
Carbon + oxygen carbon dioxide (C + O2 CO2)
Reactions of metals with oxygen
Metal + oxygen metal oxide
Reactants products
Reaction of magnesium with oxygen
Forms the product magnesium oxide
2Mg + O2 2MgO
Produces a bright white light which can damage your eyes when burning. The end product
is a white powder
Reaction of iron with oxygen
A metal like iron will gradually react with oxygen in the atmosphere to form a metal oxide
e.g. iron oxide
Iron reacts easily with oxygen to form rust
Water and oxygen are required for iron to rust
2 types of iron oxide form:
• 4Fe + 3O2 2Fe2O3 = Rust
• 3Fe + 2O2 Fe3O4 = Magnetite
Rusting
Occurs on the surface of iron
Iron is in contact with oxygen and moisture/water
Rusting is a type of corrosion where metal is damaged or weakened
Reactive metals corrode quicker (group 1)
Non-reactive metals will not corrode even after many years (closer to zig-zag line on the
periodic table) such as gold or platinum
Preventing Rust
Galvanise
covering with another metal that does not rust so easily
Electroplating or chrome plating
process of electrolysis
deposits thin layer of chromium (more reactive metal)
forms shiny, attractive surfaces
Paint
prevents metal contact with water/moisture and oxygen
Bars that protect ships (sacrificial anodes)
connecting/adding more reactive metal bars (magnesium alloys or zinc)
bars corrode first
Oiling
oil repels water (oil is hydrophobic)
Reactions of non-metals with oxygen
Non-metal + oxygen non-metal oxide
Reactants product
Carbon + oxygen carbon dioxide (C + O2 CO2)