Sports Science
Topic 1 - Anatomy and physiology
Joint Flexibility
-range of movement
-needed to perform everyday activity
-gives us exibility
- exibility deteriorates with age
-no movement = no synovial uid = sti joints
-staying active and stretching regularly prevents
loss of mobility
-Joint exibility is the term used to describe the
Range Of Motion (ROM) possible in each planes of
motion in a joint
-how much a person can move around a joint is their
exibility
-when a segment or part of the body moves, it rotates
on an imaginary axis
-ROM is measured in degrees with a geniometer
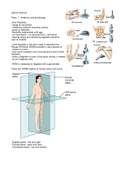
There are THREE planes of motion which we move:
-Sagittal plane - left and right
-Frontal plane - back and front
-Transverse plane - top and bottom
flfl fl fl fl ff
, Joint Flexibility
- Static exibility is the ROM present when a body segment is passively moved by a partner.
Muscles stretch and get more exible without her doing the work.
Dynamic exibility is the ROM achieved by actively movie a body part using muscular contraction.
The athlete is doing the work.
Flexibility is joint speci c ie. lots of exibility at one joint doesn’t mean that all the joints will be
equally exible.
Di erent factors will in uence an athlete’s joint Flexibility:
-The of the bone surface - some bone shapes naturally don’t allow a lot of movement eg. Flat
bones.
-The amount of muscle present
-The amount of fatty tissue present - these two are similar. If there is a lot of muscle or a lot of fat
around a joint it will limit movement.
Athletes that are involved in bilateral asymmetry (where one limb is used more often than the
other) eg. Tennis, will nd they have less ROM for the dominant arm because the muscles are
bigger and this restricts some movements.
Risk of injury is higher when joint exibility is very low (sti ), very high (too loose) or imbalance
between dominant and non dominant sides of the body.
The chances of getting injured is more likely if:
- You are too sti - tear muscles
- You are too exible - joints keep dislocating
Limited joint Flexibility isn’t good because the collagenous tissues and muscles crossing the joint
are tight - the chances of their joint tearing or rupturing if the joint is forced beyond its normal
ROM increases.
Large bulky muscles will decrease joint ROM but strong, stable joints enable large ROMs.
ff
fl fl fl fl ff fiflfi fl fl fl ff
Topic 1 - Anatomy and physiology
Joint Flexibility
-range of movement
-needed to perform everyday activity
-gives us exibility
- exibility deteriorates with age
-no movement = no synovial uid = sti joints
-staying active and stretching regularly prevents
loss of mobility
-Joint exibility is the term used to describe the
Range Of Motion (ROM) possible in each planes of
motion in a joint
-how much a person can move around a joint is their
exibility
-when a segment or part of the body moves, it rotates
on an imaginary axis
-ROM is measured in degrees with a geniometer
There are THREE planes of motion which we move:
-Sagittal plane - left and right
-Frontal plane - back and front
-Transverse plane - top and bottom
flfl fl fl fl ff
, Joint Flexibility
- Static exibility is the ROM present when a body segment is passively moved by a partner.
Muscles stretch and get more exible without her doing the work.
Dynamic exibility is the ROM achieved by actively movie a body part using muscular contraction.
The athlete is doing the work.
Flexibility is joint speci c ie. lots of exibility at one joint doesn’t mean that all the joints will be
equally exible.
Di erent factors will in uence an athlete’s joint Flexibility:
-The of the bone surface - some bone shapes naturally don’t allow a lot of movement eg. Flat
bones.
-The amount of muscle present
-The amount of fatty tissue present - these two are similar. If there is a lot of muscle or a lot of fat
around a joint it will limit movement.
Athletes that are involved in bilateral asymmetry (where one limb is used more often than the
other) eg. Tennis, will nd they have less ROM for the dominant arm because the muscles are
bigger and this restricts some movements.
Risk of injury is higher when joint exibility is very low (sti ), very high (too loose) or imbalance
between dominant and non dominant sides of the body.
The chances of getting injured is more likely if:
- You are too sti - tear muscles
- You are too exible - joints keep dislocating
Limited joint Flexibility isn’t good because the collagenous tissues and muscles crossing the joint
are tight - the chances of their joint tearing or rupturing if the joint is forced beyond its normal
ROM increases.
Large bulky muscles will decrease joint ROM but strong, stable joints enable large ROMs.
ff
fl fl fl fl ff fiflfi fl fl fl ff