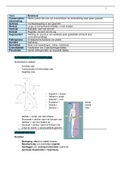
Mitosi
• responsible for the growth and regeneration of worn tissue of an
organis
• cells develop from existing cell
• in order to grow + develop organisms need additional cell
• new cells formed by division of existing cell
• type of division is called mitosis or mitotic cell divisio
• after cells formed, go through differentiation (changes in structure) and
become specialised for certain functio
Tissues
Groups of cells of similar structure that perform particular function
Study of tissues called histology
Egg cell Sperm cell
FERTILIZATION
Zygote
In animal, embryonic
tissue undergoes 2 types of tissues in living
repeated mitosis and organisms
differentiation to form
a foetus or new MITOSIS • embryonic / meristematic
organism (undifferentiated
Embryo • permanent tissue
In a plant, embryonic
tissue is called (specialised)
meristematic tissue.
CELL SPECIALISATION
AND DIFFERENTIATION
m
.
:
)
s
s
.
n
s
n
s
.
, • all cells contain hereditary information in the form of chromosomes in the
nucleu
• chromosomes are made of DNA and protei
• a chromosome is a linear arrangement of gene
• each gene carries one piece of hereditary informatio
• each species has its own number of chromosomes
• humans have 46 (23 pairs) of chromosomes
Diagram of the nucleus
Functions
1. controls all cell activitie
2. carries hereditary material in the form of chromosome
3. plays a role in the synthesis of protein
• if cells are to divide, chromosomes must be doubled so that the daughter cells
can contain exactly the same information as the mother cel
• doubling of material occurs during a phase in the life cycle of the cells called the
interphase (12-24 hour period before mitosis starts). Cell manufactures extra
energy to last through mitosis.
•DNA replication: the doubling of
chromosome
•the original strand and the ‘replica’ are held
together by tissue called a centromere. The
DNA strands are now called chromatids
s
s
:
s
:
s
.
n
s
n
s
l
• responsible for the growth and regeneration of worn tissue of an
organis
• cells develop from existing cell
• in order to grow + develop organisms need additional cell
• new cells formed by division of existing cell
• type of division is called mitosis or mitotic cell divisio
• after cells formed, go through differentiation (changes in structure) and
become specialised for certain functio
Tissues
Groups of cells of similar structure that perform particular function
Study of tissues called histology
Egg cell Sperm cell
FERTILIZATION
Zygote
In animal, embryonic
tissue undergoes 2 types of tissues in living
repeated mitosis and organisms
differentiation to form
a foetus or new MITOSIS • embryonic / meristematic
organism (undifferentiated
Embryo • permanent tissue
In a plant, embryonic
tissue is called (specialised)
meristematic tissue.
CELL SPECIALISATION
AND DIFFERENTIATION
m
.
:
)
s
s
.
n
s
n
s
.
, • all cells contain hereditary information in the form of chromosomes in the
nucleu
• chromosomes are made of DNA and protei
• a chromosome is a linear arrangement of gene
• each gene carries one piece of hereditary informatio
• each species has its own number of chromosomes
• humans have 46 (23 pairs) of chromosomes
Diagram of the nucleus
Functions
1. controls all cell activitie
2. carries hereditary material in the form of chromosome
3. plays a role in the synthesis of protein
• if cells are to divide, chromosomes must be doubled so that the daughter cells
can contain exactly the same information as the mother cel
• doubling of material occurs during a phase in the life cycle of the cells called the
interphase (12-24 hour period before mitosis starts). Cell manufactures extra
energy to last through mitosis.
•DNA replication: the doubling of
chromosome
•the original strand and the ‘replica’ are held
together by tissue called a centromere. The
DNA strands are now called chromatids
s
s
:
s
:
s
.
n
s
n
s
l