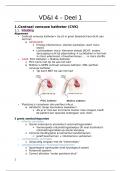
evolution
Scienti c theory based on series of hypothesis that have been tested and veri ed
over time
A chemical, matter, language, etc. a change over time
BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION:
Described as GENETIC CHANGES in a population of living organisms that have
been INHERITED over successive generations due to NATURAL SELECTION!will
eventually result in new species
2 TYPES OF BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION:
1) Macro-evolution
➢ Development of new life forms/species from earlier life forms
➢ Happens over many generations!extended geological periods
➢ Speciation forms basis of macro-evolution
2) Micro-evolution
➢ Variation that occurs within a species
➢ Small changes orientate in gene pool!results in small changes in genotype
of species
➢ Changes are passed onto the offspring
VARIATION
SPECIES:
Group of closely related organisms that have similar characteristics, can interbreed
and produce fertile offspring
POPULATION:
Total number of individuals of a particular species that live in a particular area at a
particular time so that they can randomly mate with each other.
C O N T R I B U T I O N S TO VA R I AT I O N A M O N G I N D I V I D U A L S O F T H E
S AME SPECIES:
1)MEIOSIS
➢ Crossing over!exchange of genetic material during prophase of Meoisis
➢ Results in 4 unique gametes!all have different gene combinations
➢ Random arrangement of homologous pairs on equator!happens during
Metaphase I
➢ Results in greater variation amongst gametes
, 2) MUTATIONS
➢ May change DNA!leads to formation of new characteristic
➢ New characteristic!helps organism adapt to environment and survive
➢ Mutation needs to occur in gamete to be passed onto offspring
3) CHANCE OF FERTILIZATION
➢ Combination of male & female gametes!completely random
➢ Result in new gene combination every time fertilization occurs!leads to
more variation
4) RANDOM MATING
➢ Male and females mate randomly
➢ Results in variety of gene combinations!more variation in species
TYPES OF VARIATION
CONTINOUS VARIATIO DISCONTINUOUS VARIATIO
Range of phenotypes for particular Phenotypes t into separate categories
characteristics with no intermediate forms
o Controlled by many genes o Controlled by single set of genes
o Very LARGE 1 extreme to the other o Few distinct types
o Environmental factors effect o Environmental factors don’t effect
variations as well variation
o Eg: height, skin colour, mass of Eg: sex, tongue rolling, blood groups
newborn babies
EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTIO
1.FOSSILS:
Form in layers of SEDIMENTARY ROCK as the hard parts of the body fossilize under
only SPECIFIC CONDITIONS (NO O2 , rapid burial & high pressure)
− Provide evidence for history of extinct organisms
− Indicate climate and environmental conditions
− Provide order in which organisms evolve
− Gaps in fossil record!mostly where there is a change from one organism to
another
Scienti c theory based on series of hypothesis that have been tested and veri ed
over time
A chemical, matter, language, etc. a change over time
BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION:
Described as GENETIC CHANGES in a population of living organisms that have
been INHERITED over successive generations due to NATURAL SELECTION!will
eventually result in new species
2 TYPES OF BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION:
1) Macro-evolution
➢ Development of new life forms/species from earlier life forms
➢ Happens over many generations!extended geological periods
➢ Speciation forms basis of macro-evolution
2) Micro-evolution
➢ Variation that occurs within a species
➢ Small changes orientate in gene pool!results in small changes in genotype
of species
➢ Changes are passed onto the offspring
VARIATION
SPECIES:
Group of closely related organisms that have similar characteristics, can interbreed
and produce fertile offspring
POPULATION:
Total number of individuals of a particular species that live in a particular area at a
particular time so that they can randomly mate with each other.
C O N T R I B U T I O N S TO VA R I AT I O N A M O N G I N D I V I D U A L S O F T H E
S AME SPECIES:
1)MEIOSIS
➢ Crossing over!exchange of genetic material during prophase of Meoisis
➢ Results in 4 unique gametes!all have different gene combinations
➢ Random arrangement of homologous pairs on equator!happens during
Metaphase I
➢ Results in greater variation amongst gametes
, 2) MUTATIONS
➢ May change DNA!leads to formation of new characteristic
➢ New characteristic!helps organism adapt to environment and survive
➢ Mutation needs to occur in gamete to be passed onto offspring
3) CHANCE OF FERTILIZATION
➢ Combination of male & female gametes!completely random
➢ Result in new gene combination every time fertilization occurs!leads to
more variation
4) RANDOM MATING
➢ Male and females mate randomly
➢ Results in variety of gene combinations!more variation in species
TYPES OF VARIATION
CONTINOUS VARIATIO DISCONTINUOUS VARIATIO
Range of phenotypes for particular Phenotypes t into separate categories
characteristics with no intermediate forms
o Controlled by many genes o Controlled by single set of genes
o Very LARGE 1 extreme to the other o Few distinct types
o Environmental factors effect o Environmental factors don’t effect
variations as well variation
o Eg: height, skin colour, mass of Eg: sex, tongue rolling, blood groups
newborn babies
EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTIO
1.FOSSILS:
Form in layers of SEDIMENTARY ROCK as the hard parts of the body fossilize under
only SPECIFIC CONDITIONS (NO O2 , rapid burial & high pressure)
− Provide evidence for history of extinct organisms
− Indicate climate and environmental conditions
− Provide order in which organisms evolve
− Gaps in fossil record!mostly where there is a change from one organism to
another