LIFE PROCESSES IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
Endocrine system:
System of chemical messengers comprising feedback loops of hormones released by internal glands directly into the
bloodstream.
→ works by a system called chemical co-ordination:
Slow, prolonged process of communicating information throughout the body using hormones
- Horomone:
> chemical substance
> used to carry information from one part of the body to another
> regulates metabolic functions
Properties of a hormone:
> Proteins – insulin, thyroxin. Fats- Steroids – testosterone.
> Powerful in small concentrations.
> Very short life.
> Can stimulate target cells to release another hormone.
> Does not operate in isolation but in conjunction with other hormones and the CNS.
Types of glands:
Endocrine Exocrine
Photo
Ducts Ductless Has ducts
Secretions Secrete directly into blood stream Secrete into organ/external environment
Response Delayed Instant
Functioning of a hormone:
- Endocrine releases hormone
- Travel in blood to target organ
- Bind to receptors on the target organ
Effect is not long lasting
If a gland produces too much of a hormone the gland is HYPERACTIVE.
If a gland does not produce enough hormones the gland is HYPOACTIVE.
Homeostasis:
Keeping the internal environment (like water, salt, temperature, and glucose levels) constant.
, - Describes the mechanism by which a constant internal environment is maintained
The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment despite changes in the external environment
Flow diagram of control of homeostasis:
Feedback loops
1) Positive feedback loop:
The product (effect) of a reaction leads to an increase in that reaction.
- A positive feedback loop moves a system further away from the target of equilibrium.
2) Negative feedback loop:
Negative feedback operates if the system is disturbed
- It sets off a sequence of events which counteract (opposite or negative to) the disturbance and tends to
restore the system to its original state.
- Negative feedback is therefore the mechanism by which animals maintain a constant state.
The role of a negative feedback in maintaining homeostasis:
This loop works by reversing or counteracting a stimulus that causes a change, ultimately returning the system to its
desired state and preventing extreme fluctuations.
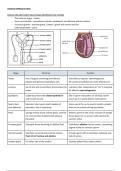
Endocrine glands and the hormones secreted by them:
The brain:
1) The hypothalamus
2) The pituitary gland