Endocrine Gland
Secretory cells of endocrine glands release their products, signaling molecules called hormones, into the neighboring
vascularized compartment for uptake by capillaries and distribution throughout the body.
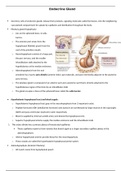
Pituitary gland (hypophysis)
o Lies on the sphenoid bone, in sella
turcica.
o The anterior part arises from the
hypophyseal (Rathke) pouch from the
roof of the primitive mouth.
o Neurohypophysis consists of a large part,
the pars nervosa, and the smaller
infundibulum stalk attached to the
hypothalamus at the median eminence.
o Adenohypophysis from the oral
ectoderm has 3 parts: pars distalis (anterior lobe), pars tuberalis, and pars intermedia adjacent to the posterior
pars nervosa.
o The pituitary gland is composed of an anterior part and a posterior part that is directly attached to the
hypothalamus region of the brain by an infundibular stalk.
o The gland occupies a fossa of the sphenoid bone called the sella turcica
Hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract and blood supply:
o Hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract goes in the neurohypophysis from 2 important nuclei.
o Peptide hormones ADH (antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin are synthesized by large neurons in the supraoptic
(ADH) and para-ventricular (oxytocin) nuclei respectively.
o Blood is supplied by internal carotid artery and drained by hypophyseal vein.
o Superior hypophyseal arteries supply the median eminence and the infundibular stalk
1. This artery divide into a primary plexus of fenestrated capillaries
These capillaries rejoin to form venules that branch again as a larger secondary capillary plexus in the
adenohypophysis.
o Inferior hypophyseal arteries provide blood for the neurohypophysis.
o These vessels are called the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system
Adenohypophysis (Anterior Pituitary)
o All 3 parts come from hypophysisal pouch
,
Secretory cells of endocrine glands release their products, signaling molecules called hormones, into the neighboring
vascularized compartment for uptake by capillaries and distribution throughout the body.
Pituitary gland (hypophysis)
o Lies on the sphenoid bone, in sella
turcica.
o The anterior part arises from the
hypophyseal (Rathke) pouch from the
roof of the primitive mouth.
o Neurohypophysis consists of a large part,
the pars nervosa, and the smaller
infundibulum stalk attached to the
hypothalamus at the median eminence.
o Adenohypophysis from the oral
ectoderm has 3 parts: pars distalis (anterior lobe), pars tuberalis, and pars intermedia adjacent to the posterior
pars nervosa.
o The pituitary gland is composed of an anterior part and a posterior part that is directly attached to the
hypothalamus region of the brain by an infundibular stalk.
o The gland occupies a fossa of the sphenoid bone called the sella turcica
Hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract and blood supply:
o Hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract goes in the neurohypophysis from 2 important nuclei.
o Peptide hormones ADH (antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin are synthesized by large neurons in the supraoptic
(ADH) and para-ventricular (oxytocin) nuclei respectively.
o Blood is supplied by internal carotid artery and drained by hypophyseal vein.
o Superior hypophyseal arteries supply the median eminence and the infundibular stalk
1. This artery divide into a primary plexus of fenestrated capillaries
These capillaries rejoin to form venules that branch again as a larger secondary capillary plexus in the
adenohypophysis.
o Inferior hypophyseal arteries provide blood for the neurohypophysis.
o These vessels are called the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system
Adenohypophysis (Anterior Pituitary)
o All 3 parts come from hypophysisal pouch
,