NERVOUS SYSTEM REVIEW SHEET
1. Function of the CNS and PNS
● Central Nxervous System (CNS):
Includes the brain and spinal cord. It processes and interprets sensory information and
sends out instructions (motor commands).
● Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
Includes all the nerves outside the CNS. It connects the CNS to the limbs and organs.
It’s responsible for transmitting sensory input to the CNS and carrying out motor output
from the CNS to muscles and glands.
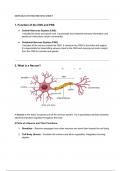
2. What is a Neuron?
A neuron is the basic functional unit of the nervous system. It’s a specialized cell that transmits
electrical impulses (signals) throughout the body.
9 Parts of a Neuron and Their Functions:
1. Dendrites – Receive messages from other neurons and send them toward the cell body.
2. Cell Body (Soma) – Contains the nucleus and other organelles; integrates incoming
signals.
, 3. Nucleus – Contains the cell’s DNA; controls the neuron’s activities.
4. Axon Hillock – Junction between the cell body and axon; where the action potential
begins.
5. Axon – Carries electrical impulses away from the cell body toward other neurons or
effectors.
6. Myelin Sheath – Fatty insulation around the axon that increases the speed of impulse
transmission.
7. Nodes of Ranvier – Gaps between myelin where the impulse jumps from node to node
(saltatory conduction).
8. Axon Terminals (Terminal Buttons) – Endings of axons; release neurotransmitters to
send messages to the next neuron.
9. Synapse – The gap between two neurons where neurotransmitters cross to transmit the
signal.
3. Types of Neurons and Directions of Signal
● Sensory Neurons: Carry information from sensory receptors (skin, eyes, etc.) toward
the CNS.
● Motor Neurons: Carry instructions from the CNS to muscles or glands (effectors).
● Interneurons: Found within the CNS, they connect sensory and motor neurons and
help with processing information.
4. Blood Supply of the Brain
The brain gets its blood from three major arteries:
1. Anterior Cerebral Artery – Supplies the front (frontal lobes).
2. Middle Cerebral Artery – Supplies the sides (temporal and parietal lobes).
1. Function of the CNS and PNS
● Central Nxervous System (CNS):
Includes the brain and spinal cord. It processes and interprets sensory information and
sends out instructions (motor commands).
● Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
Includes all the nerves outside the CNS. It connects the CNS to the limbs and organs.
It’s responsible for transmitting sensory input to the CNS and carrying out motor output
from the CNS to muscles and glands.
2. What is a Neuron?
A neuron is the basic functional unit of the nervous system. It’s a specialized cell that transmits
electrical impulses (signals) throughout the body.
9 Parts of a Neuron and Their Functions:
1. Dendrites – Receive messages from other neurons and send them toward the cell body.
2. Cell Body (Soma) – Contains the nucleus and other organelles; integrates incoming
signals.
, 3. Nucleus – Contains the cell’s DNA; controls the neuron’s activities.
4. Axon Hillock – Junction between the cell body and axon; where the action potential
begins.
5. Axon – Carries electrical impulses away from the cell body toward other neurons or
effectors.
6. Myelin Sheath – Fatty insulation around the axon that increases the speed of impulse
transmission.
7. Nodes of Ranvier – Gaps between myelin where the impulse jumps from node to node
(saltatory conduction).
8. Axon Terminals (Terminal Buttons) – Endings of axons; release neurotransmitters to
send messages to the next neuron.
9. Synapse – The gap between two neurons where neurotransmitters cross to transmit the
signal.
3. Types of Neurons and Directions of Signal
● Sensory Neurons: Carry information from sensory receptors (skin, eyes, etc.) toward
the CNS.
● Motor Neurons: Carry instructions from the CNS to muscles or glands (effectors).
● Interneurons: Found within the CNS, they connect sensory and motor neurons and
help with processing information.
4. Blood Supply of the Brain
The brain gets its blood from three major arteries:
1. Anterior Cerebral Artery – Supplies the front (frontal lobes).
2. Middle Cerebral Artery – Supplies the sides (temporal and parietal lobes).