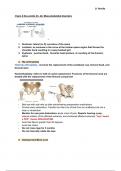
Cardiovascular System: Blood vessels and hemodynamics
21.1: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels:
Arteries: carry blood away from the heart to other organs.
Large arteries= leave heart and divide into medium sized muscular arteries
that further divide into small arteries= which in turn divide into still smaller
arteries called arterioles.
As arterioles enter a tissue= they branch into numerous tiny vessels called
blood capillaries or capillaries.
Group of capillaries within a tissue reunite to form small veins called venules.
Veins= convey blood from the tissues back to the heart.
Basic Structure of a Blood Vessel:
Consist: three layers of different tissues: an epithelial inner lining, a middle
layer consisting of smooth muscle and elastic connective tissue and a
connective tissue covering outer covering.
Three layers: innermost to outermost:
Tunica interna (intima)
Tunica media, and
Tunica externa (adventita).
Tunica Interna:
Forms the inner lining of the blood vessel= directly in contact with the blood
that flows through the lumen.
,Innermost layer= endothelium= continuous with the endocardial lining of the
heart.
Thin layer of flattened cells that lines the inner surface of the entire
cardiovascular system.
Actively participate in variety of vessel-related activities, including physical
influences on blood flow, secretion of locally acting chemical mediators-
influence the contractile state of the vessel’s overlying smooth muscle and
assistance with capillary permeability.
Smooth muscle luminal surface= facilitates efficient blood flow by reducing
surface friction.
Second compartment= basement membrane= deep to endothelium.
Provides physical support base for epithelial layer.
Framework of collagen fibres- affords the basement membrane - significant
tensile strength= properties provide resilience for stretching and recoil.
Outermost layer= internal elastic lamina.
Thin sheet of elastic fibres with variable number of windowlike openings=
looks like Swiss cheese.
Openings= facilitate diffusion of materials through tunica interna to thicker
tunica media.
Tunica Media:
Muscular and connective tissue layer= displays the greatest variation among
the different vessel types.
Increase in sympathetic stimulation= stimulates smooth muscles to
contract= squeezing the diameter of the lumen. Decreased diameter- called
vasoconstriction.
As sympathetic stimulation decreases, or in the presence of certain
chemicals (like nitric oxide, H+ and lactic acid) or in response to blood
pressure, smooth muscle fibres relax= resulting in vasodilation= lumen
diameter increases.
Vascular spasm= smooth muscle contracts when a small artery or arteriole=
damaged= limits blood loss.
,Tunica media and tunica externa= separated by network of elastic fibres=
external elastic lamina= part of tunica media.
Tunica Externa:
Outer covering of a blood vessel= consists of elastic and collagen fibres.
Small vessels= supply tissue of vessel wall with blood= vaso vasorum.
Tunica externa= helps anchor the vessels to the surroundings.
Arteries:
Walls of arteries= three layers
Due to their plentiful elastic fibres, arteries normally have high compliance=
their walls easily stretch or expand without tearing in response to a small
increase in pressure.
Elastic Arteries:
Largest arteries in the blood.
Characterised by well-defined internal and external elastic laminae= along
with a tunica media=dominated by elastic fibres called elastic lamellae.
Two major trunks= exit the heart (aorta and pulmonary trunk), along with
aorta’s major initial branches such as brachiocephalic, subclavian, common
carotid and common iliac arteries.
Important functions:
Help propel blood onward while ventricles are relaxing.
As blood is ejected from heart= their walls stretch, easily accommodating
the surge of blood.
Elastic fibres momentarily store mechanical energy= functioning as a
pressure reservoir. Then, the elastic fibres recoil and convert stored potential
energy into kinetic energy of the blood.
, Because they conduct blood from the heart to medium-sized, more muscular
arteries, elastic arteries= conducting arteries.
Muscular Arteries:
Medium sized=called muscular as their tunica media contains more smooth
muscle fibres and less elastic fibres than elastic arteries.
Relatively thick because large amt of smooth muscle makes the walls of
muscular arteries relatively thick.
Capable of vasoconstriction and vasodilation to control blood flow.
As they branch and ultimately distribute blood to each of the various
organs= called distributing arteries. Eg: brachial artery in arm; radial artery
in forearm.
Tunica externa= thicker in muscular arteries
The ability of the muscle to contract and maintain a state of partial
contraction= vascular tone.
Stiffens the vessel walls and is important in maintaining vessel pressure and
efficient blood flow.
Anastomoses:
The union of branches of two or more arteries supplying the same region of
the body = anastomosis.
Provide alternate routes for blood to reach a tissue or organ.
The alternate route of blood flow to a body part through an anastomosis =
collateral circulation.
Anastomosis= may occur between veins and between arterioles and
venules.
Arteries= do not anastomose= end arteries.
Arterioles:
21.1: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels:
Arteries: carry blood away from the heart to other organs.
Large arteries= leave heart and divide into medium sized muscular arteries
that further divide into small arteries= which in turn divide into still smaller
arteries called arterioles.
As arterioles enter a tissue= they branch into numerous tiny vessels called
blood capillaries or capillaries.
Group of capillaries within a tissue reunite to form small veins called venules.
Veins= convey blood from the tissues back to the heart.
Basic Structure of a Blood Vessel:
Consist: three layers of different tissues: an epithelial inner lining, a middle
layer consisting of smooth muscle and elastic connective tissue and a
connective tissue covering outer covering.
Three layers: innermost to outermost:
Tunica interna (intima)
Tunica media, and
Tunica externa (adventita).
Tunica Interna:
Forms the inner lining of the blood vessel= directly in contact with the blood
that flows through the lumen.
,Innermost layer= endothelium= continuous with the endocardial lining of the
heart.
Thin layer of flattened cells that lines the inner surface of the entire
cardiovascular system.
Actively participate in variety of vessel-related activities, including physical
influences on blood flow, secretion of locally acting chemical mediators-
influence the contractile state of the vessel’s overlying smooth muscle and
assistance with capillary permeability.
Smooth muscle luminal surface= facilitates efficient blood flow by reducing
surface friction.
Second compartment= basement membrane= deep to endothelium.
Provides physical support base for epithelial layer.
Framework of collagen fibres- affords the basement membrane - significant
tensile strength= properties provide resilience for stretching and recoil.
Outermost layer= internal elastic lamina.
Thin sheet of elastic fibres with variable number of windowlike openings=
looks like Swiss cheese.
Openings= facilitate diffusion of materials through tunica interna to thicker
tunica media.
Tunica Media:
Muscular and connective tissue layer= displays the greatest variation among
the different vessel types.
Increase in sympathetic stimulation= stimulates smooth muscles to
contract= squeezing the diameter of the lumen. Decreased diameter- called
vasoconstriction.
As sympathetic stimulation decreases, or in the presence of certain
chemicals (like nitric oxide, H+ and lactic acid) or in response to blood
pressure, smooth muscle fibres relax= resulting in vasodilation= lumen
diameter increases.
Vascular spasm= smooth muscle contracts when a small artery or arteriole=
damaged= limits blood loss.
,Tunica media and tunica externa= separated by network of elastic fibres=
external elastic lamina= part of tunica media.
Tunica Externa:
Outer covering of a blood vessel= consists of elastic and collagen fibres.
Small vessels= supply tissue of vessel wall with blood= vaso vasorum.
Tunica externa= helps anchor the vessels to the surroundings.
Arteries:
Walls of arteries= three layers
Due to their plentiful elastic fibres, arteries normally have high compliance=
their walls easily stretch or expand without tearing in response to a small
increase in pressure.
Elastic Arteries:
Largest arteries in the blood.
Characterised by well-defined internal and external elastic laminae= along
with a tunica media=dominated by elastic fibres called elastic lamellae.
Two major trunks= exit the heart (aorta and pulmonary trunk), along with
aorta’s major initial branches such as brachiocephalic, subclavian, common
carotid and common iliac arteries.
Important functions:
Help propel blood onward while ventricles are relaxing.
As blood is ejected from heart= their walls stretch, easily accommodating
the surge of blood.
Elastic fibres momentarily store mechanical energy= functioning as a
pressure reservoir. Then, the elastic fibres recoil and convert stored potential
energy into kinetic energy of the blood.
, Because they conduct blood from the heart to medium-sized, more muscular
arteries, elastic arteries= conducting arteries.
Muscular Arteries:
Medium sized=called muscular as their tunica media contains more smooth
muscle fibres and less elastic fibres than elastic arteries.
Relatively thick because large amt of smooth muscle makes the walls of
muscular arteries relatively thick.
Capable of vasoconstriction and vasodilation to control blood flow.
As they branch and ultimately distribute blood to each of the various
organs= called distributing arteries. Eg: brachial artery in arm; radial artery
in forearm.
Tunica externa= thicker in muscular arteries
The ability of the muscle to contract and maintain a state of partial
contraction= vascular tone.
Stiffens the vessel walls and is important in maintaining vessel pressure and
efficient blood flow.
Anastomoses:
The union of branches of two or more arteries supplying the same region of
the body = anastomosis.
Provide alternate routes for blood to reach a tissue or organ.
The alternate route of blood flow to a body part through an anastomosis =
collateral circulation.
Anastomosis= may occur between veins and between arterioles and
venules.
Arteries= do not anastomose= end arteries.
Arterioles: