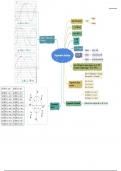
nucleotide nitrogenous bases
Phosphate (form weak
DNA Replication -
> hydrogen bonds)
& ↳ cytosine =↳ Guanine
Backbone Base ↳ Adenine ↳
↳
=
Chromosome Thymine
I or uracil
Sugar -
> Yonly
in RNA
( mere
DNA
& >
↳
-
RiboseNA) #
car-garage
Apple-Free
-
Pere si
a
chromatin Histone Double helix structure
(Identical DNA) z
wraps around histone
to form a chromosome
Gene
A Parent strand is 5 DNA ↳codes for
Specific
unwinded or unzipped
= 12 NA
Proteins
using heicase
able
3M
3
&
A Primase starts gl
replication by DNA VS RNA
placing
a short piece of 12NA =
on
↳ free
the 3 end of strand
nucleotides bond DNA
min
in a order ↳ ↳ Ribose
complementary unzip Deoxyribose
using
Polymerase ↳ A = TC = G ↳ A = UG = C
↳ within nucleus
) ↳ nucleus +
fM
-
skazaki
Polymerase Joins fragment
- Ribosomes B
- -
the and
sugar phosphate - cytoplasm
groups to create two
-
↳ only comes ↳ mRNA + RNA
, ,
Identical strands US BNA rI2NA , miRNA
daughter
↳ ↳ stores and transmits information
ligase
-
acts as give
to bind the of the sI ↳ Directs cell processes
gaps 3 Free nucleotides
Okazaki semi Conservative ↳ per menent ↳
together Te m p o r a r y
*
·
A two strands are m DNA In
Eukaryotic Cells
⑭
us
created each with prokaryotic cell,
·
a conserved and
u G Di
·
mus
new strand Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
l ↳ Double stranded
helix ↳ Doble stranded helix
a
nucleo a
*
m
↳
Within ↳ Within nucleus
⑳ =
single circular multiple linear
Y
M
ad Strand
newstrand - ↳
may have
↳ Also within Chloroplast
old Strand and
Plasmids mitochondred
, Transcriptioninside nucleus -
Protein f A
copy of the
coding
Synthesis DDNADable helix strand is
created by
a MINA Strand
Protein function eunzippin merase
& DNA Double helix closes
↳
Enzyme- Catalyst
↳ Antibodies immune defence
B
-
↳ Tr a n s p o r t -
assist movement
J
&
carrior
accross cell membrane
S
↳ Hormones -
creates cell Affect
-mini
·
Protein Structure
Primary
sequence
·
*
Secondary structure
Structure
of Amino
Hydrogen bonds between
g
Acids -
Polypeptide
chain
Amino Acids
d mRNA
into
Strand
introns (non
is broken
coding)
S
-
mRNA
Te m p l a t e
(2) B exons
(coding) introns
d -
⑳
Beta pleeted
M she is
exons are bonded
3D
Te r t i a r y
Shape
Structure
formed
Interactions between amino acids
due to
secondary
± translation
back
-
together
outside nucleus
g - mature MRNA
A MINA leaves nucleus
Idisulfide)
D vior Channel -
into
& Chydrogen) -±
MRNA
= ±
Ribosome
the cytoplasm
g mRNA travels to
the ribosome ↳
structure
Quaternary
bonded
&
Two or more
polypeptide chains
together-creates unique shape
afunction of protein
l MRNA is fed through Premiu
the ribosome
l
· D
18 ltrend Anticodon)
-
⑩ When fed
through M mRNA
Notes :
a FINA
the codon
is bonded (condon)
to
⑪ each
a
that
train
amino acid
polypeptide
-
codes for a
createin
chain
specific
ticodon ⑰ +RNA
rebond
acid
is
for
moved and
to another amino
reuse
can
Protein
⑪
Polypeptide
freeO * d
chain
T
See
⑰
· a
*
.....
-
I
MRNA
I
Stop
⑬ This process continues
Cuaa vaG Uga)
⑬ w *
Ribosome
until stop signal is found
Phosphate (form weak
DNA Replication -
> hydrogen bonds)
& ↳ cytosine =↳ Guanine
Backbone Base ↳ Adenine ↳
↳
=
Chromosome Thymine
I or uracil
Sugar -
> Yonly
in RNA
( mere
DNA
& >
↳
-
RiboseNA) #
car-garage
Apple-Free
-
Pere si
a
chromatin Histone Double helix structure
(Identical DNA) z
wraps around histone
to form a chromosome
Gene
A Parent strand is 5 DNA ↳codes for
Specific
unwinded or unzipped
= 12 NA
Proteins
using heicase
able
3M
3
&
A Primase starts gl
replication by DNA VS RNA
placing
a short piece of 12NA =
on
↳ free
the 3 end of strand
nucleotides bond DNA
min
in a order ↳ ↳ Ribose
complementary unzip Deoxyribose
using
Polymerase ↳ A = TC = G ↳ A = UG = C
↳ within nucleus
) ↳ nucleus +
fM
-
skazaki
Polymerase Joins fragment
- Ribosomes B
- -
the and
sugar phosphate - cytoplasm
groups to create two
-
↳ only comes ↳ mRNA + RNA
, ,
Identical strands US BNA rI2NA , miRNA
daughter
↳ ↳ stores and transmits information
ligase
-
acts as give
to bind the of the sI ↳ Directs cell processes
gaps 3 Free nucleotides
Okazaki semi Conservative ↳ per menent ↳
together Te m p o r a r y
*
·
A two strands are m DNA In
Eukaryotic Cells
⑭
us
created each with prokaryotic cell,
·
a conserved and
u G Di
·
mus
new strand Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
l ↳ Double stranded
helix ↳ Doble stranded helix
a
nucleo a
*
m
↳
Within ↳ Within nucleus
⑳ =
single circular multiple linear
Y
M
ad Strand
newstrand - ↳
may have
↳ Also within Chloroplast
old Strand and
Plasmids mitochondred
, Transcriptioninside nucleus -
Protein f A
copy of the
coding
Synthesis DDNADable helix strand is
created by
a MINA Strand
Protein function eunzippin merase
& DNA Double helix closes
↳
Enzyme- Catalyst
↳ Antibodies immune defence
B
-
↳ Tr a n s p o r t -
assist movement
J
&
carrior
accross cell membrane
S
↳ Hormones -
creates cell Affect
-mini
·
Protein Structure
Primary
sequence
·
*
Secondary structure
Structure
of Amino
Hydrogen bonds between
g
Acids -
Polypeptide
chain
Amino Acids
d mRNA
into
Strand
introns (non
is broken
coding)
S
-
mRNA
Te m p l a t e
(2) B exons
(coding) introns
d -
⑳
Beta pleeted
M she is
exons are bonded
3D
Te r t i a r y
Shape
Structure
formed
Interactions between amino acids
due to
secondary
± translation
back
-
together
outside nucleus
g - mature MRNA
A MINA leaves nucleus
Idisulfide)
D vior Channel -
into
& Chydrogen) -±
MRNA
= ±
Ribosome
the cytoplasm
g mRNA travels to
the ribosome ↳
structure
Quaternary
bonded
&
Two or more
polypeptide chains
together-creates unique shape
afunction of protein
l MRNA is fed through Premiu
the ribosome
l
· D
18 ltrend Anticodon)
-
⑩ When fed
through M mRNA
Notes :
a FINA
the codon
is bonded (condon)
to
⑪ each
a
that
train
amino acid
polypeptide
-
codes for a
createin
chain
specific
ticodon ⑰ +RNA
rebond
acid
is
for
moved and
to another amino
reuse
can
Protein
⑪
Polypeptide
freeO * d
chain
T
See
⑰
· a
*
.....
-
I
MRNA
I
Stop
⑬ This process continues
Cuaa vaG Uga)
⑬ w *
Ribosome
until stop signal is found