firms, agencies, and individuals subject to
environmental regulations are called .
Question 1 options:
a) abatement costs
b) enforcement costs
Suppose a manufacturing firm that is about to be
regulated faces the following actual and potential
production costs: 1)
$2,500 before regulation; 2) $2,925 in the future
without the regulation; and 3) $3,240 in the future
with the
regulation. The before/after cost of the regulation is
and the with/without cost of the regulation is .
a) $425; $740
b) $425; $315
c) $740; $315
When environmental regulation of an entire industry
results in output adjustments, the social cost of the
regulation can be measured by the changes in
consumer and producer surpluses.
True
When supply and demand are linear curves, the
incidence of the tax depends on the slopes of the
demand and supply curves.
, True
Refer to Table below. If the with/without principle
were applied to estimate the change in cost due to
a new environmental regulation, the added costs
due to the new regulation would be .
Production costs before the regulation $ 200
Production costs in the future, without the regulation $ 250
Production costs in the future, with the regulation $ 290
Question 5 options:
a) $90
b) $40
Enforcement costs for new protective programs include
Question 6 options:
a) resources devoted to monitoring the behavior of firms.
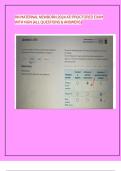
Refer to the Figure below. Panel (a) and Panel
(b) represent industries that have experienced cost
increases due to environmental regulations. Assume
that both price increases are equivalent. Which panel
reflects less impact on the consumer and a large
industry adjustment, in terms of less output?