Molecular Genetics Test Notes 2017-05-20
Hassan Alibhai Page MG1
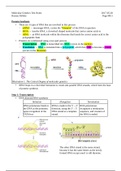
Protein Synthesis
• There are 3 types of RNA that are involved in this process
◦ mRNA → messenger RNA, carries the “blueprint” of the DNA in question
◦ tRNA → transfer RNA, a cloverleaf shaped molecule that carries amino acids to
◦ rRNA → an RNA molecule within the ribosome that bonds the correct amino acid to the
polypeptide chain
• Proteins are synthesized using a two-part process
◦ Transcription → DNA is transcribed into RNA (occurs in the nucleus)
◦ Translation → RNA is translated into a polypeptide, which then folds to become a protein
(occurs in the ribosome)
Illustration 1: The Central Dogma of molecular genetics
• tRNA loops in a cloverleaf formation to create anti-parallel DNA strands, which form the base
of protein synthesis
Step 1: Transcription
• DNA-directed RNA synthesis
Initiation Elongation Termination
RNA polymerase binds to RNA is made in the 5’→3’ RNA polymerase
the DNA at the promoter, direction, using the 3’→5’ recognizes a termination
upon recognition of the DNA strand as a template sequence, and creation of
TATA box strand. the RNA is ended.
The other DNA strand is the sense strand,
because it has the same letters as the newly
formed RNA except uracil is still thymine.
, Molecular Genetics Test Notes 2017-05-20
Hassan Alibhai Page MG2
Step 1.5: Post Transcription Modifications
• Addition of the poly-A tail → a chain of 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides, one nucleotide at a
time, to the 3’ end of the new mRNA
• Addition of the 5’ cap → seven guanine nucleotides added to the 5’ end of the new mRNA
• Introns (non-coding mRNA regions) must be removed for the mRNA to be fully functioning
and to always produce proteins, leaving only exons (coding mRNA regions)
◦ In the nucleus, a process called mRNA splicing removes the introns from pre-mRNAs and
joins the exons together.
◦ mRNA splicing occurs in a spliceosome: a complex formed between the pre-mRNA and a
handful of small ribonucleoproteins called snRNPs (pronounced snurps).
Summary of Modifications
1. Addition of the 5’
cap and the poly A
tail
2. Removal of all
introns, leaving only
protein-coding
regions
Hassan Alibhai Page MG1
Protein Synthesis
• There are 3 types of RNA that are involved in this process
◦ mRNA → messenger RNA, carries the “blueprint” of the DNA in question
◦ tRNA → transfer RNA, a cloverleaf shaped molecule that carries amino acids to
◦ rRNA → an RNA molecule within the ribosome that bonds the correct amino acid to the
polypeptide chain
• Proteins are synthesized using a two-part process
◦ Transcription → DNA is transcribed into RNA (occurs in the nucleus)
◦ Translation → RNA is translated into a polypeptide, which then folds to become a protein
(occurs in the ribosome)
Illustration 1: The Central Dogma of molecular genetics
• tRNA loops in a cloverleaf formation to create anti-parallel DNA strands, which form the base
of protein synthesis
Step 1: Transcription
• DNA-directed RNA synthesis
Initiation Elongation Termination
RNA polymerase binds to RNA is made in the 5’→3’ RNA polymerase
the DNA at the promoter, direction, using the 3’→5’ recognizes a termination
upon recognition of the DNA strand as a template sequence, and creation of
TATA box strand. the RNA is ended.
The other DNA strand is the sense strand,
because it has the same letters as the newly
formed RNA except uracil is still thymine.
, Molecular Genetics Test Notes 2017-05-20
Hassan Alibhai Page MG2
Step 1.5: Post Transcription Modifications
• Addition of the poly-A tail → a chain of 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides, one nucleotide at a
time, to the 3’ end of the new mRNA
• Addition of the 5’ cap → seven guanine nucleotides added to the 5’ end of the new mRNA
• Introns (non-coding mRNA regions) must be removed for the mRNA to be fully functioning
and to always produce proteins, leaving only exons (coding mRNA regions)
◦ In the nucleus, a process called mRNA splicing removes the introns from pre-mRNAs and
joins the exons together.
◦ mRNA splicing occurs in a spliceosome: a complex formed between the pre-mRNA and a
handful of small ribonucleoproteins called snRNPs (pronounced snurps).
Summary of Modifications
1. Addition of the 5’
cap and the poly A
tail
2. Removal of all
introns, leaving only
protein-coding
regions