HK +2270 final
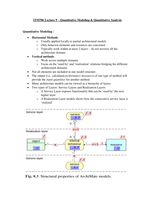
anatomical reference planes
anatomical directional terms
->
superior : closer to head
->
Sagittal plane :
Splits into left and right halves
->
-> inferior : farther from head medio-lateral axis
-> anterior :
towards the front of the body
->
posterior towards the back of
->
frontal plane Splits into front and back halves
the body
:
:
->
->
medial towards the
:
midline of the body antero-posterior axis
->
lateral :
away from the midline of the body
->
closer to the trunk
->
transverse plane Splits into top and bottom halves
proximal
:
:
->
->
distal : farther away from the trunk longitudinal axis
plane frontal plane transverse plane
Sagittal
movements movements movements
->
abduction
->
flexion
->
->
inversion pronation
->
dorsiflexion
->
-
radial deviation abduction
->
plantarflexion
->
->
adduction ->
rotations
extension
->
eversion ->
supination
->
hyperextension
->
ulnar deviation ->
adduction
solving bone on bone lever systems
1. solve for muscle forces ->
first class : load-falcrum-force
2
. solve for bone on bone forces
+ interpret results
->
speed or mechanical
. Consider joint anatomy
3 ->
second class : falcrum-load-force
->
find relevant compression and shear axis ->
mechanical advantage
->
break bone on bone forces into components
->
third class : falcrum-force-load
speed advantage
->
link segment systems location of COM
1. draw FBD
guess positive given Coordinates of distal and
->
,
for forces +
moment prox:
. solve
2 for net forces and moments
->
COMx=Xprox+ (Xdistal Xprox) · Rprox -
. draw
3 FBD next to adjacent segment .
At the ->
COMy=Yprox + (Ydistal Yprox)· Reprox
-
connecting joint ,
draw net joint rxn moment ->
given multiple COMs :
equal in magnitude but opposite in direction -
COMx= M . X, +
MzX , /M
4. draw the moments that are caused by each
->
COMy= M Y
.
,
+
MeYe/M
of the net "cut"
joint at the m=segment of total body
->
rxn forces mass
segment -> M =
mass of segment
,
anatomical reference planes
anatomical directional terms
->
superior : closer to head
->
Sagittal plane :
Splits into left and right halves
->
-> inferior : farther from head medio-lateral axis
-> anterior :
towards the front of the body
->
posterior towards the back of
->
frontal plane Splits into front and back halves
the body
:
:
->
->
medial towards the
:
midline of the body antero-posterior axis
->
lateral :
away from the midline of the body
->
closer to the trunk
->
transverse plane Splits into top and bottom halves
proximal
:
:
->
->
distal : farther away from the trunk longitudinal axis
plane frontal plane transverse plane
Sagittal
movements movements movements
->
abduction
->
flexion
->
->
inversion pronation
->
dorsiflexion
->
-
radial deviation abduction
->
plantarflexion
->
->
adduction ->
rotations
extension
->
eversion ->
supination
->
hyperextension
->
ulnar deviation ->
adduction
solving bone on bone lever systems
1. solve for muscle forces ->
first class : load-falcrum-force
2
. solve for bone on bone forces
+ interpret results
->
speed or mechanical
. Consider joint anatomy
3 ->
second class : falcrum-load-force
->
find relevant compression and shear axis ->
mechanical advantage
->
break bone on bone forces into components
->
third class : falcrum-force-load
speed advantage
->
link segment systems location of COM
1. draw FBD
guess positive given Coordinates of distal and
->
,
for forces +
moment prox:
. solve
2 for net forces and moments
->
COMx=Xprox+ (Xdistal Xprox) · Rprox -
. draw
3 FBD next to adjacent segment .
At the ->
COMy=Yprox + (Ydistal Yprox)· Reprox
-
connecting joint ,
draw net joint rxn moment ->
given multiple COMs :
equal in magnitude but opposite in direction -
COMx= M . X, +
MzX , /M
4. draw the moments that are caused by each
->
COMy= M Y
.
,
+
MeYe/M
of the net "cut"
joint at the m=segment of total body
->
rxn forces mass
segment -> M =
mass of segment
,