Module 1.5
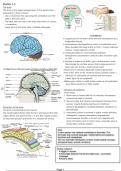
The brain
The brain is the upper enlarged part of the spinal chord
enclosed by a bony cranium
• Like a mushroom the cap being the cerebellum and the
stalk is the brain stem
• The back near the top of the brain stem there is a bump
= cerebellum
• Lower part of the brain stem = Medulla oblongata
A.Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain dived into two hemispheres by a
longitudinal ssure
Hemispheres held together by mass of myelinated nerve
bres bundled into large tracts to form = corpus callosum
(corpus = body callosum= white)
Joining provides for communication between
hemispheres and between cerebral cortex and lower part
of CNS
Surface is made up of folds ( gyri ) and grooves ( sulci)
that enlarge the surface area so that a large amount of
brain cells can t into a small cranial cavity
There are 4 ventricles lled with cerebro-spinal uid
The outer 3mm of the cerebrum forms cerebral cortex =
collection of cell bodies of neurons and forms grey
matter (grey bc of cytoplasm)
Below grey matter is white matter made up of myelinated
nerve bres (white bc of fatty myelin)
Functions of cerebrum
Three areas:
1. Motor area in frontal lobe for all voluntary movements
(consciously able to control)
2. Sensory areas that receive and interpret impulses from
sensory organs (hearing, tasting and smelling in
Protection of the brain temporal lobe)(sight in occipital lobe)(skin sensations in
The brain is protected by the cranium parietal lobe)
The cerebrospinal uid is uid found in and around the CNS 3. Associative cortex is involved in higher mental activities
organs (brain and spinal chord) = it acts like a liquid cushion (intelligence, memory, perception, language and
so they have buoyant protection in a situation of trauma. consciousness) function is to sort out, integrate and
store info before sent to motor areas. Associate area in
frontal lobe controls emotion
Note:
In each person one cerebral hemisphere is dominate. The
dominate side controls language, mathematical and analytical
functions and handedness.
The non dominate hemisphere controls simple spatial concepts
(recognize faces, sounds, emotions)
Corpus collosum
- is bigger in women
- Is the bridge between the left and right brain = processes
messages
- And joins lobes
fi
fi fi fi fl fi fl fl Page 1
The brain
The brain is the upper enlarged part of the spinal chord
enclosed by a bony cranium
• Like a mushroom the cap being the cerebellum and the
stalk is the brain stem
• The back near the top of the brain stem there is a bump
= cerebellum
• Lower part of the brain stem = Medulla oblongata
A.Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain dived into two hemispheres by a
longitudinal ssure
Hemispheres held together by mass of myelinated nerve
bres bundled into large tracts to form = corpus callosum
(corpus = body callosum= white)
Joining provides for communication between
hemispheres and between cerebral cortex and lower part
of CNS
Surface is made up of folds ( gyri ) and grooves ( sulci)
that enlarge the surface area so that a large amount of
brain cells can t into a small cranial cavity
There are 4 ventricles lled with cerebro-spinal uid
The outer 3mm of the cerebrum forms cerebral cortex =
collection of cell bodies of neurons and forms grey
matter (grey bc of cytoplasm)
Below grey matter is white matter made up of myelinated
nerve bres (white bc of fatty myelin)
Functions of cerebrum
Three areas:
1. Motor area in frontal lobe for all voluntary movements
(consciously able to control)
2. Sensory areas that receive and interpret impulses from
sensory organs (hearing, tasting and smelling in
Protection of the brain temporal lobe)(sight in occipital lobe)(skin sensations in
The brain is protected by the cranium parietal lobe)
The cerebrospinal uid is uid found in and around the CNS 3. Associative cortex is involved in higher mental activities
organs (brain and spinal chord) = it acts like a liquid cushion (intelligence, memory, perception, language and
so they have buoyant protection in a situation of trauma. consciousness) function is to sort out, integrate and
store info before sent to motor areas. Associate area in
frontal lobe controls emotion
Note:
In each person one cerebral hemisphere is dominate. The
dominate side controls language, mathematical and analytical
functions and handedness.
The non dominate hemisphere controls simple spatial concepts
(recognize faces, sounds, emotions)
Corpus collosum
- is bigger in women
- Is the bridge between the left and right brain = processes
messages
- And joins lobes
fi
fi fi fi fl fi fl fl Page 1