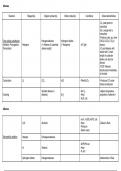
Reaction Reagent(s) Organic product(s) Other product(s) Conditions Observations/Notes
-Cl2: pale-green to
colourless
-Br2: orange-red to
colourless
-Products vary, eg. more
Free radical substitution Halogenoalkanes Hydrogen halides CHCl3 & CCl4 if Cl2 in
(Initiation, Propagation, Halogens (+ Alkanes x2 substrate (+ Halogens) -UV light excess
Termination) alkane length) -Cl2 and alkanes with
double the C chain
length of substrate
alkane can also be
formed
-TEST: Alkenes
decolourise immediately
in the dark
Combustion O2 CO2 H2O -Plentiful O2 -Produces CO under
limited combustion
Smaller alkenes (+ -No O2 -Higher temperature,
Cracking alkanes) (H2) -Heat proportion of alkenes +
-Al2O3 cat.
Alkenes
-conc. H2SO4/H3PO4 cat.
H2O Alcohols -Heat -Zeitsev’s Rule
-Pressure
-Steam used
Electrophilic addition Halogen Dihalogenoalkanes
-Ni/Pt/Pd cat.
H2 Alkanes -Heat
-H2 dry
Hydrogen halides Halogenoalkanes -Markovnikov’s Rule
, -Purple to colourless
-Cold -Brown if acid present
Alkandiols -Dilute -TEST: Alkanes do not
(H2O needed = reagent) -Acidic change colour
Oxidation KMnO4
-CO2 H2O -Hot -CO2: 2H
-Carboxylic acids -Concentrated -Carboxylic Acids: 1H + 1
-Ketones -Acidic alkyl
-Ketones: 2 alkyls
Free radical addition Polymer alkanes -Heat
polymerisation -Pressure
-Catalyst
Halogenoalkanes
Reaction Reagent(s) Organic product(s) Other product(s) Conditions Observations/Notes
-Reflux -Faster than hydrolysis
Hydroxides -Heat due to OH full formal -
Alcohol -Aqueous charge
H2O -Reflux
Nucleophilic substitution -Reflux
(SN2: 1o, SN1: 3o) Cyanides Nitriles Halides -Heat
-Excess cyanide
-Alcoholic
-Reflux
-Heat
NH3 1o amines -Excess NH3
-Alcoholic
-Pressure
-Reflux
Elimination Hydroxides Alkenes H2O + Halides -Heat -Zeitsev’s Rule
-Alcoholic