Lecture 2 – Animal Development – ABS 224.3
Development in triploblastic Organisms
• Fertilization
o Zygote
• Cleavage
o Morula
• Gastrulation
o Gastrula
• Organogenesis
o Neurla
• Neurulation
Organogenesis and Terminal
Differentiation
• Growth produces more and/or larger cells.
• Developmental produces organisms with a defined set of characteristics by cell differentiation.
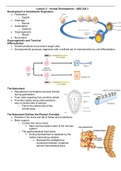
The Notochord
• Mesodermal rod-shaped structure formed
during gastrulation.
• From cells migrating from primitive streak
• Provides rigidity along anteroposterior
axis on dorsal side of embryo.
o Forms the central axis of the
animal body.
The Notochord Defines the Phylum Chordata
• Persists in the trunk and tail of fishes and amphibians.
• Body support:
o Contain the nerve chord.
§ Main communication stem of the nervous
system
o The gastrointestinal tract below.
§ During development is replaced by the
hollow interlocking vertebra
• Because the cartilaginous
substance between vertebrae
termed intervertebral discs.
,Neurulation
• The first major event of organogenesis
o The transformation of neural plate
• Start with a thickening of the ectoderm located along
the dorsal midline of the embryo termed neural plate
that give rise to:
o The neural tube
o Neural crest
o On both sides develops the epidermis
• The embryo at the stage is termed neurula.
Neural Tube Formation
• The neural plate folds into the neural tube.
o Differentiates into the spinal cord and the brain,
forming the central nervous system.
• The neural crest differentiates into:
o The peripheral and enteric neurons,
o Glial cells. Of the nervous system
During neurulation, the body develop into segments with specialized functions.
• Termed somite or primitive segments
• A set of bilaterally paired blocks mesoderm
o Form along the head-to-tail axis is segmented animals.
§ Gives rise to the cells of vertebrae and ribs, and define it
as repeated structures.
Ganglia as primitive sensory organs & pacemakers
• Are clusters of nerve cell bodies.
• Function like relay station
• Ganglia evolved into a primitive eye,
o The ocelli
• In jellyfish ganglia function as pacemakers
• In jellyfish ganglia also evolved into statocyst.
o Fluid-filled sacs with solid particles termed statolith.
The NS of Echinoderms
• Echinoderms are marine radially symmetric animals.
• They do not have a true CNS.
o Ocelli are primitive light detection organs based on pigments.
The true central nervous system evolved with bilateral symmetry in segmented animals.
• Segmentation is the division of the body plans into a series of repetitive segments.
o Characteristic of arthropods, annelids and chordata
Cephalization
• Big part of nervous system evolutionary history highly specialized structure
• An evolutionary trend in which the mouth and sense organs become concentrated at the front
end of an animal.
Advantages of Cephalization
• Sensory information about the environment is initially detected in the anterior region.
o Detect images, developed learning abilities and memory and ultimately self-awareness.
The vertebrate’s nervous system
• Latin, vertebrates, “back boned”
• Comprise all animals with an internal skeleton.
• All vertebrates are built along the basic chordate body plan that comprise:
o The skull
, o A vertebral column
o The spinal cord
o Ganglia
o Nerves
The vertebrate’s central nervous system
• Divided into two major parts, the brain, and the
spinal cord.
• The brain lies within the skill and consists of four
principal parts:
o Brain stem:
§ Midbrain
§ Pons
§ Medulla oblongata
o Cerebrum
o Cerebellum
• Diencephalon
o Thalamus
§ Above
o Hypothalamus
§ Below
The hypothalamus
• Devices from the diencephalon
• Located below the thalamus, extend to the pituitary gland.
o Pituitary gland - Base of the brain
o Forming the posterior pituitary gland, or neurohypophysis
The Vertebral Column and the Spinal Cord
• The vertebral column, spinal column, or spine
o A long tube-like structure composed of a series of bone segments termed vertebrae (31
in humans) that extends from the skull to the coccyx.
§ It encloses a central canal that contains cerebrospinal fluid.
Development in triploblastic Organisms
• Fertilization
o Zygote
• Cleavage
o Morula
• Gastrulation
o Gastrula
• Organogenesis
o Neurla
• Neurulation
Organogenesis and Terminal
Differentiation
• Growth produces more and/or larger cells.
• Developmental produces organisms with a defined set of characteristics by cell differentiation.
The Notochord
• Mesodermal rod-shaped structure formed
during gastrulation.
• From cells migrating from primitive streak
• Provides rigidity along anteroposterior
axis on dorsal side of embryo.
o Forms the central axis of the
animal body.
The Notochord Defines the Phylum Chordata
• Persists in the trunk and tail of fishes and amphibians.
• Body support:
o Contain the nerve chord.
§ Main communication stem of the nervous
system
o The gastrointestinal tract below.
§ During development is replaced by the
hollow interlocking vertebra
• Because the cartilaginous
substance between vertebrae
termed intervertebral discs.
,Neurulation
• The first major event of organogenesis
o The transformation of neural plate
• Start with a thickening of the ectoderm located along
the dorsal midline of the embryo termed neural plate
that give rise to:
o The neural tube
o Neural crest
o On both sides develops the epidermis
• The embryo at the stage is termed neurula.
Neural Tube Formation
• The neural plate folds into the neural tube.
o Differentiates into the spinal cord and the brain,
forming the central nervous system.
• The neural crest differentiates into:
o The peripheral and enteric neurons,
o Glial cells. Of the nervous system
During neurulation, the body develop into segments with specialized functions.
• Termed somite or primitive segments
• A set of bilaterally paired blocks mesoderm
o Form along the head-to-tail axis is segmented animals.
§ Gives rise to the cells of vertebrae and ribs, and define it
as repeated structures.
Ganglia as primitive sensory organs & pacemakers
• Are clusters of nerve cell bodies.
• Function like relay station
• Ganglia evolved into a primitive eye,
o The ocelli
• In jellyfish ganglia function as pacemakers
• In jellyfish ganglia also evolved into statocyst.
o Fluid-filled sacs with solid particles termed statolith.
The NS of Echinoderms
• Echinoderms are marine radially symmetric animals.
• They do not have a true CNS.
o Ocelli are primitive light detection organs based on pigments.
The true central nervous system evolved with bilateral symmetry in segmented animals.
• Segmentation is the division of the body plans into a series of repetitive segments.
o Characteristic of arthropods, annelids and chordata
Cephalization
• Big part of nervous system evolutionary history highly specialized structure
• An evolutionary trend in which the mouth and sense organs become concentrated at the front
end of an animal.
Advantages of Cephalization
• Sensory information about the environment is initially detected in the anterior region.
o Detect images, developed learning abilities and memory and ultimately self-awareness.
The vertebrate’s nervous system
• Latin, vertebrates, “back boned”
• Comprise all animals with an internal skeleton.
• All vertebrates are built along the basic chordate body plan that comprise:
o The skull
, o A vertebral column
o The spinal cord
o Ganglia
o Nerves
The vertebrate’s central nervous system
• Divided into two major parts, the brain, and the
spinal cord.
• The brain lies within the skill and consists of four
principal parts:
o Brain stem:
§ Midbrain
§ Pons
§ Medulla oblongata
o Cerebrum
o Cerebellum
• Diencephalon
o Thalamus
§ Above
o Hypothalamus
§ Below
The hypothalamus
• Devices from the diencephalon
• Located below the thalamus, extend to the pituitary gland.
o Pituitary gland - Base of the brain
o Forming the posterior pituitary gland, or neurohypophysis
The Vertebral Column and the Spinal Cord
• The vertebral column, spinal column, or spine
o A long tube-like structure composed of a series of bone segments termed vertebrae (31
in humans) that extends from the skull to the coccyx.
§ It encloses a central canal that contains cerebrospinal fluid.