Lecture 2
Cell:
- A cell is the smallest unit of life
- Continually carries out metabolic activities essential for life,
as well as specialized function and adapts to changing
conditions
- Form organs and organ system
- Genes control a cell’s action and response
- Different in cell shape makes different function
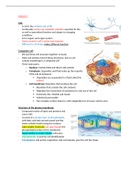
Composite cell
- We put these cell structure together to study
- Most cell contain most of these structures, but no cell
contain everything in a composite cell
- Three main parts:
o Nucleus: Contain DNA and direct cells activity
o Cytoplasm: Organelles and fluid make up the majority
if the cell (in between)
Organelles are suspended in a fluid called the
cytosol
o Cell membrane: Boundary that encloses the cell
Boundary that contain the cell contents
Regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell
Extremely thin, flexible and elastic
Selectively permeable
Has complex surface features; with adaptations to increase surface area
Structure of the plasma membrane
- Composed mainly of lipids and proteins and
some CHO
- Consists of a double layer of phospholipids,
with fatty acid tails turned inward and the
water-soluble heads facing the surfaces
- Lipid soluble molecules can pass though the
phospholipid portion of the membrane
- Impermeable to water soluble molecules
- Glycoproteins is used for cell identification
- Cytoskeleton will anchor supportive rods and tubules; give the cell the shape
Cell:
- A cell is the smallest unit of life
- Continually carries out metabolic activities essential for life,
as well as specialized function and adapts to changing
conditions
- Form organs and organ system
- Genes control a cell’s action and response
- Different in cell shape makes different function
Composite cell
- We put these cell structure together to study
- Most cell contain most of these structures, but no cell
contain everything in a composite cell
- Three main parts:
o Nucleus: Contain DNA and direct cells activity
o Cytoplasm: Organelles and fluid make up the majority
if the cell (in between)
Organelles are suspended in a fluid called the
cytosol
o Cell membrane: Boundary that encloses the cell
Boundary that contain the cell contents
Regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell
Extremely thin, flexible and elastic
Selectively permeable
Has complex surface features; with adaptations to increase surface area
Structure of the plasma membrane
- Composed mainly of lipids and proteins and
some CHO
- Consists of a double layer of phospholipids,
with fatty acid tails turned inward and the
water-soluble heads facing the surfaces
- Lipid soluble molecules can pass though the
phospholipid portion of the membrane
- Impermeable to water soluble molecules
- Glycoproteins is used for cell identification
- Cytoskeleton will anchor supportive rods and tubules; give the cell the shape