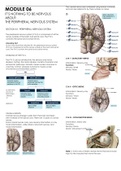
The cranial nerves are numbered using roman numerals,
MODULE 06 and can be referred to by their number or name.
IT’S NOTHING TO BE NERVOUS
ABOUT:
THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
SECTION 01: PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The peripheral nervous system (P N S) is composed of all the
nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. The P N S
contains the spinal and cranial nerves.
Interesting Fact
As you may recall from Module 05, the peripheral nervous system
(P N S) is composed of all the nerves outside of the brain and spinal
cord. The P N S contains the spinal and cranial nerves.
DIVISIONS OF THE P N S
C N I – OLFACTORY NERVE
The P N S can be divided into the sensory and motor
divisions. Further, the motor division consists of somatic and Information: Sensory only
autonomic pathways. Somatic means under conscious or Function:
voluntary control, whereas autonomic means under Sensory: Smell
unconscious or involuntary control. Motor: None
C N II – OPTIC NERVE
Information: Sensory only
Function:
Sensory: Vision
Motor: None
CRANIAL NERVES
Cranial nerves emerge in pairs from the brain and brain
stem instead of the spinal cord. There are 12 pairs of cranial C N III – OCULOMOTOR NERVE
nerves.
Some cranial nerves carry only sensory information or only Information: Motor only
motor information, while others carry both sensory and Function:
motor information. Sensory: None
Motor: Movement of the eye
Note: C N III is one of three cranial nerves that send motor
input to the muscles that move the eye.
, C N IV – TROCHLEAR NERVE C N VIII – VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR NERVE
Information: Motor only Information: Sensory only
Function: Function:
Sensory: None Sensory: Equilibrium and hearing
Motor: Movement of the eye Motor: None
Note: This is the second of three cranial nerves involved in
eye movement.
C N V – TRIGEMINAL NERVE C N IX - GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE
Information: Sensory and motor Information: Sensory and motor
Functions: Functions:
Sensory: Forehead, eye, Sensory: Sensory innervation
upper jaw, lower jaw of the pharynx,
Motor: Muscles of mastication taste from posterior 1/3 tongue
Motor: Pharynx muscles,
parasympathetic innervation
of salivary glands
INTERESTING FACT What is the other C N involved in taste?
C N V has three divisions, therefore the “tri” in trigeminal is logical. Facial or C N VII
Knowing that C N V (trigeminal) provides motor innervation C N X – VAGUS NERVE
to the muscles of mastication, which muscle would C N V
innervate? Information: Sensory and motor
Masseter Functions:
Sensory: Sensory innervation of the larynx
Motor: Pharynx and larynx muscles,
C N VI - ABDUCENS NERVE
parasympathetic innervation
of the thoracic and abdominal organs
Information: Motor only
Function:
Sensory: None
Motor: Movement of the eye
C N XI – ACCESSORY NERVE
Information: Motor only
Function:
Note: This is the third cranial nerve involved in eye Sensory: None
movement. Motor: Trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles
C N VII – FACIAL NERVE
Information: Sensory and motor
Functions:
Sensory: Taste for anterior 2/3 of tongue
Motor: Muscles of facial expression,
parasympathetic innervation
of tear and salivary glands
MODULE 06 and can be referred to by their number or name.
IT’S NOTHING TO BE NERVOUS
ABOUT:
THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
SECTION 01: PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The peripheral nervous system (P N S) is composed of all the
nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. The P N S
contains the spinal and cranial nerves.
Interesting Fact
As you may recall from Module 05, the peripheral nervous system
(P N S) is composed of all the nerves outside of the brain and spinal
cord. The P N S contains the spinal and cranial nerves.
DIVISIONS OF THE P N S
C N I – OLFACTORY NERVE
The P N S can be divided into the sensory and motor
divisions. Further, the motor division consists of somatic and Information: Sensory only
autonomic pathways. Somatic means under conscious or Function:
voluntary control, whereas autonomic means under Sensory: Smell
unconscious or involuntary control. Motor: None
C N II – OPTIC NERVE
Information: Sensory only
Function:
Sensory: Vision
Motor: None
CRANIAL NERVES
Cranial nerves emerge in pairs from the brain and brain
stem instead of the spinal cord. There are 12 pairs of cranial C N III – OCULOMOTOR NERVE
nerves.
Some cranial nerves carry only sensory information or only Information: Motor only
motor information, while others carry both sensory and Function:
motor information. Sensory: None
Motor: Movement of the eye
Note: C N III is one of three cranial nerves that send motor
input to the muscles that move the eye.
, C N IV – TROCHLEAR NERVE C N VIII – VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR NERVE
Information: Motor only Information: Sensory only
Function: Function:
Sensory: None Sensory: Equilibrium and hearing
Motor: Movement of the eye Motor: None
Note: This is the second of three cranial nerves involved in
eye movement.
C N V – TRIGEMINAL NERVE C N IX - GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE
Information: Sensory and motor Information: Sensory and motor
Functions: Functions:
Sensory: Forehead, eye, Sensory: Sensory innervation
upper jaw, lower jaw of the pharynx,
Motor: Muscles of mastication taste from posterior 1/3 tongue
Motor: Pharynx muscles,
parasympathetic innervation
of salivary glands
INTERESTING FACT What is the other C N involved in taste?
C N V has three divisions, therefore the “tri” in trigeminal is logical. Facial or C N VII
Knowing that C N V (trigeminal) provides motor innervation C N X – VAGUS NERVE
to the muscles of mastication, which muscle would C N V
innervate? Information: Sensory and motor
Masseter Functions:
Sensory: Sensory innervation of the larynx
Motor: Pharynx and larynx muscles,
C N VI - ABDUCENS NERVE
parasympathetic innervation
of the thoracic and abdominal organs
Information: Motor only
Function:
Sensory: None
Motor: Movement of the eye
C N XI – ACCESSORY NERVE
Information: Motor only
Function:
Note: This is the third cranial nerve involved in eye Sensory: None
movement. Motor: Trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles
C N VII – FACIAL NERVE
Information: Sensory and motor
Functions:
Sensory: Taste for anterior 2/3 of tongue
Motor: Muscles of facial expression,
parasympathetic innervation
of tear and salivary glands