Save
Students also studied
final Exam 4 Study Guide 18.5 Population dynamics Ecolog
29 terms 40 terms 11 terms 22 terms
h2vmgftwmx Preview maddieleguizamo07 Preview sosaj11 Preview nbo
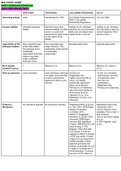
Point sampling Used to estimate how much of an area is covered by plants.
Involves choosing a number if points within an area (either randomly or in a
systemic grid)
How does point sampling work? 1. At each chosen point, record whether it hits a particular plant species
2. Count how many times the points land on that species
3 Express the total as a percentage of the total points measured
Line Sampling Data is collected along a straight line
Every plant that touches the line is recorded.
Strengths of Line Sampling 1. Provides a detailed record of vegetation along a gradient or across an area.
2. Useful for showing how species distribution changes across an environment.
Weaknesses of Line Sampling Very time-consuming, because every plant along the line must be noted.
Area or Quadrant Sampling A quadrant or square frame is placed on the ground to mark out a sample area for
study
What can Area/Quadrant Sampling be used for 1. Counting number of individual plants, or individuals of a specific species
2. Recording the number of different species (species richness)
3. Estimating percentage cover (how much of the quadrant is covered by a
species)
Limitations of Area/Quadrant Sampling 1. Estimation can lead to bias, miscalculation, and unreliable data
2. Requires good species identification skills, especially when plants look very
similar.
Benefits of Area/Quadrant Sampling Quick, easy, inexpensive method of ecological surveys