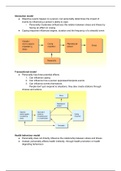
Chapter 6 & 7
Chapter 6: stress
Stress: a negative emotional experience accompanied by predictable biochemical,
physiological, cognitive and behavioural changes that are directed either toward altering the
stressful event or accommodating its effects
Stressor: stressful events
Person-environment fit: determines stress
Fight or flight response: bodily is rapidly aroused when it perceives a threat (SNS and
endocrine) either mobilizing organism or fleeing danger
Fight: aggressive response to stress
Flight: removal of social situations, alcohol/drug use
General adaptation syndrome: when an organism is stressed, it mobalizes itself
Tend-and-befriend: theory of stress responses; in addition to fight or flight, humans respond
to stress with social and nurturant behaviour
Primary appraisal: when individuals confront a new or changing environment, they engage in
a process of primary appraisal to determine the meaning of the event
Secondary appraisal process: the assessment of one’s coping abilities and resources and
whether or not they are sufficient to meet the harm, threat and challenge of the event
Reactivity: the degree of change that occurs in the autonomic, neuroendocrine and immune
responses as a result of stress
Allostatic load: the fats that physiological systems within the body fluctuate to meet demands
from stress, a state called allostasis
Dimensions of stressful events
● Negative events: traffic ticket, finding a job…
● Uncontrollable events
● Ambiguous events
● Overload
Chronic strain: if stressful event becomes a chronic part of environment
After-effects of stress: decreases in performance or attention span
Acute stress paradigm: finds that when people are induced to perform stressful tasks they
show both short-term psychological distress and strong indications of sympathetic activity
and neuroendocrine responses
Stressful life events: cataclysmic events (death of spouse) to more mundane events
(moving)
, Daily hassles: minor stressful events and their cumulative impact on health and illness
Perceived stress: measured by a scale (like daily strain)
Role conflict: when a person receives conflicting info about work tasks or standards from
different individuals
work-life balance
Work-life conflict: occurs mainly when work interferes with family life
Stress is in the eye of the beholder
Chapter 7: moderators of the stress experience
Coping: thoughts and behaviours used to manage the internal and external demands of
situations that are appraised as stressful
Negative affectivity: pervasive negative mood marked by anxiety, depression and hostility
Pessimistic explanatory style: characteristically explain the negative events of their lives in
terms of internal, stable and global quantities of themselves
Perfectionism: setting a preoccupation with excessively high standards accompanied by a
tendency to engage in self-criticism
Dispositional optimism: general expectancy that good things will happen in the future
Self-compassion: on quality that many help buffer the negative effects of stress as well as
enhavne other health-related outcomes
Gratitude: having an orientation toward noticing and appreciating the positive in life
Psychological control: belief that one can determine one's own behaviour, influence
someone’s environment and bring about desired outcomes
Coping style: general propensity to deal with stressful events in a particular way, which can
be differential from coping strategies, which are specific behaviours, thoughts and emotions
people use to deal with a particular stressor
Avoidant (minimizing coping style) or approach (confrontive) coping style
Problem-focused coping: involves attempts to do something constructive about the stressful
conditions that are harming, threatening or challenging an individual
Emotion-focused coping: efforts to regulate emotions experiences because of the stressful
event
Dyadic coping: the interplay of stress experiences and expressed by one partner and the
coping reactions of another
Chapter 6: stress
Stress: a negative emotional experience accompanied by predictable biochemical,
physiological, cognitive and behavioural changes that are directed either toward altering the
stressful event or accommodating its effects
Stressor: stressful events
Person-environment fit: determines stress
Fight or flight response: bodily is rapidly aroused when it perceives a threat (SNS and
endocrine) either mobilizing organism or fleeing danger
Fight: aggressive response to stress
Flight: removal of social situations, alcohol/drug use
General adaptation syndrome: when an organism is stressed, it mobalizes itself
Tend-and-befriend: theory of stress responses; in addition to fight or flight, humans respond
to stress with social and nurturant behaviour
Primary appraisal: when individuals confront a new or changing environment, they engage in
a process of primary appraisal to determine the meaning of the event
Secondary appraisal process: the assessment of one’s coping abilities and resources and
whether or not they are sufficient to meet the harm, threat and challenge of the event
Reactivity: the degree of change that occurs in the autonomic, neuroendocrine and immune
responses as a result of stress
Allostatic load: the fats that physiological systems within the body fluctuate to meet demands
from stress, a state called allostasis
Dimensions of stressful events
● Negative events: traffic ticket, finding a job…
● Uncontrollable events
● Ambiguous events
● Overload
Chronic strain: if stressful event becomes a chronic part of environment
After-effects of stress: decreases in performance or attention span
Acute stress paradigm: finds that when people are induced to perform stressful tasks they
show both short-term psychological distress and strong indications of sympathetic activity
and neuroendocrine responses
Stressful life events: cataclysmic events (death of spouse) to more mundane events
(moving)
, Daily hassles: minor stressful events and their cumulative impact on health and illness
Perceived stress: measured by a scale (like daily strain)
Role conflict: when a person receives conflicting info about work tasks or standards from
different individuals
work-life balance
Work-life conflict: occurs mainly when work interferes with family life
Stress is in the eye of the beholder
Chapter 7: moderators of the stress experience
Coping: thoughts and behaviours used to manage the internal and external demands of
situations that are appraised as stressful
Negative affectivity: pervasive negative mood marked by anxiety, depression and hostility
Pessimistic explanatory style: characteristically explain the negative events of their lives in
terms of internal, stable and global quantities of themselves
Perfectionism: setting a preoccupation with excessively high standards accompanied by a
tendency to engage in self-criticism
Dispositional optimism: general expectancy that good things will happen in the future
Self-compassion: on quality that many help buffer the negative effects of stress as well as
enhavne other health-related outcomes
Gratitude: having an orientation toward noticing and appreciating the positive in life
Psychological control: belief that one can determine one's own behaviour, influence
someone’s environment and bring about desired outcomes
Coping style: general propensity to deal with stressful events in a particular way, which can
be differential from coping strategies, which are specific behaviours, thoughts and emotions
people use to deal with a particular stressor
Avoidant (minimizing coping style) or approach (confrontive) coping style
Problem-focused coping: involves attempts to do something constructive about the stressful
conditions that are harming, threatening or challenging an individual
Emotion-focused coping: efforts to regulate emotions experiences because of the stressful
event
Dyadic coping: the interplay of stress experiences and expressed by one partner and the
coping reactions of another