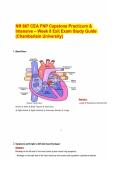
ANSWERS WELL ILLUSTRATED.
1. You are caring for a patient with a suspected stroke whose symptoms
started 2 hours ago. The CT was normal with no sign of hemorrhage. The
patient does not have any contraindications to fibrinolytic therapy. Which
treatment is best?
a. start fibrinolytic therapy ASAP
b. hold fibrinolytic therapy for 24 hours
c. order an echo before fibrinolytic administration
d. wait for MRI result: a. start fibrinolytic therapy ASAP
2. For STEMI pt, maximum goal time for ED door-to-balloon-inflation time for
PCI?
a. 150 mins
b. 180 mins
c. 120 mins
d. 90 mins: 90 mins
3. Which is the recommended oral dose of ASA for a pt w/ suspected ACS?
a. 81 mg
b. 325-650 mg
c. 160-325 mg
d. 40 mg: 160-325 mg
4. chest compressions during for adult rate: 100-120/min
5. effect of excessive ventilation
a. decresed cardiac output
b. decreased intrathoracic pressure
c. increased perfusion pressure
d. increased venous return: decreased cardiac output
6. temperature to achieve targeted temperature management after cardiac
arrest: 32-36C
7. 3 mins into cardiac arrest resuscitation attempt, one member of your team
inserts an endotracheal tube while another performs chest compressions.
Capnography shows a persistent waveform & a PETCO2 of 8mmHg. What is
the significance of the finding?
a. chest compression may not be effective
b. The endotrachael tube is in the esophagus
c. the team is ventilating the patient too often
1/7
, d. the patient meets the criteria for termination of efforts: a. chest compression
may not be effective
8. Your patient is in cardiac arrest and has been intubated. to assess CPR
quality, you should: monitor the patient's PETCO2
2/7