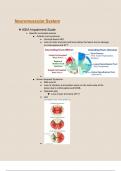
❖ASIA Impairment Scale
➢ Specific incomplete lesions
■ Anterior cord syndrome
● Cervical flexion MOI
● Loss of motor and pain and temp below the lesion due to damage
to corticospinal and STT
●
■ Brown Sequard Syndrome
● Stab wound
● Loss of vibratory and position sense on the same side at the
lesion due to corticospinal and DCML.
● Opposite side:
◆ Loss of pain and temp (STT)
● rare
●
, ■ Cauda equina injuries
● Occur below L1
● Peripheral nerve injury
● Flaccidity
● Areflexia
● Impairment of bowel and bladder
■ Central cord syndrome
● Cervical hyperextension
● STT, DCML, CST
● UE impaired > than LE
● Motor > sensory
■ Posterior cord
● DCML affected
◆ Loss of 2 point discrimination, stereognosis, proprioception
● Motor function preserved
➢Spinal cord injury tests and measures
■ ASIA impairment scale
●
● Key muscles tested
, ◆
● Sensory Test for light touch and pinprick
◆
, ● Potential complications of SCI
◆ DVT
➢ Due to decrease in pumping action
➢ Symptoms
■ Swelling LE
■ Pain and warmth over clot area
◆ autonomic dysreflexia
➢ T6 and above lesions
➢ Check cath
➢ Stay sitting
➢ Supine is contraindicated
◆ Ectopic bone
➢ Heterotopic ossification
◆ OH
◆ Pressure ulcers
◆ Spasticity
➢ Autonomic Dysreflexia + Conus medullaris (L1-L2 , LMN and UMN)
■ https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1dgRw9VQyEWM2sap01Kf9lQKk
GjTdxL6SsN_eNcdUcWA/edit#slide=id.gb3e65def20_0_18
■ https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1XXEiNuFmB-gYgbzM-hLdZQtUc
0yjtR9ED5GoK_cjwv4/edit#slide=id.p10
■ Study Guide (Neuro)
❖Balance
➢ Somatosensory Input (proprioceptive)
■ Ligaments, joints, muscles
■ Examining pt balancing on different surface
➢ Visual input
■ Closing and open eyes
➢ Vestibular
■ CNS
■ Movement of head in relation to gravity
■ Examining balance with movement of head and eye motion
❖ Balance reflexes
➢ Vestibulo Ocular reflex (VOR)
■ Allows for head and eye movement coordination
■ Gaze stabilization
➢ Vestibulospinal reflex
■ Stabilize body and control movement
■ Assists with stability while head is moving and coordination of trunk in
upright postures
➢ Automatic postural strategies
■ Ankle strategy
● 1st used
● Contract distal to proximal to control sway