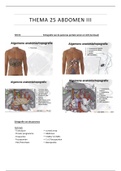
Chapter 2
CELLS AND TISSUES
CELL
THREE MAIN PARTS OF A CELL
• Plasma Membrane- cell boundary selectively
permeable & regulates movement of substances
into and out of the cell
• Cytoplasm- region between nucleus and plasma
membrane
consists of: cytosol (mostly water), cytoskeleton,
organelles
• Nucleus- controls metabolic activity,
reproduction
ORGANELLES
ribosomes – protein synthesis,
endoplasmic reticulum (rough e.r. - protein
synthesis & smooth e.r. - steroid synthesis)
Golgi apparatus – packaging, secretion;
membrane growth
mitochondria – power house
lysosomes – enzyme container
CYTOSKELETON
microtubules, microfilaments - cell movement,
support for organelles
CELL REPRODUCTION- the nucleus controls when and how the cell reproduces (i.e., by mitosis or meiosis)
Mitosis Meiosis
most body cells reproduce this way (2n→ 2n, 2n) occurs only during production of
original cells divides to become two daughter cells each identical to the parent cell Gametes
Occurs most rapidly original cell divides into two daughter
In adult connective tissue, rate of mitosis varies cells each with half the chromosome
In general, adult nervous and muscle tissue does not undergo mitosis number of the parent cell ( 2n→ n,n)
BODY TISSUES
EPITHELIAL TISSUE – CONNECTIVE TISSUE –
Covering and lining tissue Binds other tissues together
FUNCTIONS – protects, synthesizes, secretes, absorbs FUNCTIONS – support, protection, transport, storage, repair
CHARACTERISTICS – cells tightly packed CHARACTERISTICS - cells separated by Extracellular matrix
one apical (unattached) surface, one basal surface (extracellular fluid)
attached to basement membrane matrix consists of fibers, ground substance; structure varies
cells reproduce rapidly greatly
not vascularized tissue type depends on cell type
MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION fibroblasts produce fibers and ground substance
• Squamous - flat
• Cuboidal – cube shaped TYPES OF FIBERS:
CELLS AND TISSUES
CELL
THREE MAIN PARTS OF A CELL
• Plasma Membrane- cell boundary selectively
permeable & regulates movement of substances
into and out of the cell
• Cytoplasm- region between nucleus and plasma
membrane
consists of: cytosol (mostly water), cytoskeleton,
organelles
• Nucleus- controls metabolic activity,
reproduction
ORGANELLES
ribosomes – protein synthesis,
endoplasmic reticulum (rough e.r. - protein
synthesis & smooth e.r. - steroid synthesis)
Golgi apparatus – packaging, secretion;
membrane growth
mitochondria – power house
lysosomes – enzyme container
CYTOSKELETON
microtubules, microfilaments - cell movement,
support for organelles
CELL REPRODUCTION- the nucleus controls when and how the cell reproduces (i.e., by mitosis or meiosis)
Mitosis Meiosis
most body cells reproduce this way (2n→ 2n, 2n) occurs only during production of
original cells divides to become two daughter cells each identical to the parent cell Gametes
Occurs most rapidly original cell divides into two daughter
In adult connective tissue, rate of mitosis varies cells each with half the chromosome
In general, adult nervous and muscle tissue does not undergo mitosis number of the parent cell ( 2n→ n,n)
BODY TISSUES
EPITHELIAL TISSUE – CONNECTIVE TISSUE –
Covering and lining tissue Binds other tissues together
FUNCTIONS – protects, synthesizes, secretes, absorbs FUNCTIONS – support, protection, transport, storage, repair
CHARACTERISTICS – cells tightly packed CHARACTERISTICS - cells separated by Extracellular matrix
one apical (unattached) surface, one basal surface (extracellular fluid)
attached to basement membrane matrix consists of fibers, ground substance; structure varies
cells reproduce rapidly greatly
not vascularized tissue type depends on cell type
MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION fibroblasts produce fibers and ground substance
• Squamous - flat
• Cuboidal – cube shaped TYPES OF FIBERS: