ANIMALS
What are the key developmental cues used to categorize early splits in animal evolution?
Specialized tissues, bilateral symmetry & triploblastic vs radial symmetry & diploblastic, body cavity, protostome
vs deuterostome.
What is bilateral symmetry and why is it important?
Bilaterally symmetric animals, have 3 tissue layers; advantages: formation of head and tail, more thorough
nervous system.
What are the key developments in the evolution of fish?
Lungs, limbs, and feet.
When did animals move to land? What adaptations were needed to thrive on land?
Arthropods first (~450mya), vertebrates later (~365mya).
What was a key transitional fossil related to the transition between fish and tetrapod? Where was it found?
Tiktaalik aka “fishapod”; Canadian arctic.
What is the phylogenetic relationship between birds, mammals and reptiles?
Mammals diverged from stem reptiles early in amniote evolution; all are amniotes.
What are the key shared derived characters of mammals?
Mammary glands, hair, fat layer under skin, high metabolic rate(endothermy), differentiated teeth, single boned
jaw, three ear bones.
What is the basic phylogeny of primates?
What two aspects of human evolution have received the most attention?
1. Bipedal walking and upright stance (Australopithecus and descendants).
2. Larger brains and ability to make stone tools (homo).
, GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
• What was Geoffroy’s view of the relationship between vertebrates and arthropods?
Arthropods are essentially upside-down vertebrates that live insider their vertebrae and walk on their ribs.
• What is evo-devo and how does it relate to the modern synthesis?
Evolutionary-developmental biology; not sure but modern synthesis = genes->organism and central dogma: DNA
>RNA->protein
Great debate of 1830 related to the discovery of transcription factors related to inversion theory.
• What is the relationship between Hox genes, inversion theory, and transcription factors?
Hox genes provide positional information in the embryo, transforming growth factor-beta inhibits nerve tissue
growth, inverted in arthropods in comparison to chordates.
• Why do many evolutionary changes alter developmental timing?
Timing of developmental events due to interactions between master genes.
Master genes must not be changed too much or organism is not viable.
Gene duplication…mutations can affect one version and change function without drastically changing program.
Heterochrony- evolutionary change in the rate of timing of developmental events.
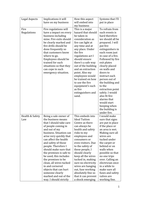
• What are some of the basic distinction in growth patterns of plants and animals?
Feature Plants Animals
Pattern of growth Often can grow continuously Tend to grow to a maximum size
How growth happens Mainly by cell enlargement (increase in Increasing the number of cells
cell size)
Where cell division Mainly at meristems – found at the tips In most tissues
happens of shoots and roots
Cell differentiation Many cells can differentiate Most cells lose the ability to
differentiate at an early stage
• What is the difference between primary and secondary growth in plants?
Primary growth- occurs in apical meristems (tips of shoots and roots), elongates shoots and roots, apical
meristem.
Secondary growth- occurs in lateral meristems: vascular cambium and cork cambium, adds thickness to woody
plants.
• What are the meristem tissues that give rise to growth in plants?
Shoot and root tip, vascular and cork cambium.
• Describe the process of elongation during primary growth in shoots.