RATED 100% CORRECT.
What are the 3 approaches to Public Administration? correct answers 1. Managerial
2. Political
3. Legal
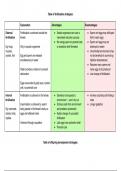
Describe the organizational structure, view of an individual, cognitive approach,
responsiveness, budgeting and decision making that takes place in a MANAGERIAL
approach to Public Administration? correct answers OS- Pluralism; bureaucracy
specialization and hierarchy
Voi-Impersonal
CA-Scientific approach; exploring hyptheses through colelction of data
Budg- Rational-building cost-effectiveness into budgets
DM- Rational-consider all plausible alternatives and choose most cost effective choice
Describe the organizational structure, view of an individual, cognitive approach,
responsiveness, budgeting and decision making that takes place in a POLITICAL approach to
Public Administration? correct answers OS- Pluralism-creation of diff groups to competeto
represent
Voi- Members of a larger group
CA- Representiveness and Responsiveness
Budg- Incrementalism-budget is a base for next year's allocations
DM- Incrementalism-because of various political orientated restraints, decisions have to be
made in increments
Describe the organizational structure, view of an individual, cognitive approach,
responsiveness, budgeting and decision making that takes place in a LEGAL approach to
Public Administration? correct answers OS- Adversary Procedure-two sides bringing
evidence to support their positions
Voi- Unique person in specific set of circumstances
CA- Adjudication-mock trial case to find out truth
Budg- Funding to protect Consitutional Integrity and Rights
DM- Incremental- the facts from each new case are evaluated in light of previous cases
What is the Hatch Act? correct answers The Hatch Act of 1939 is a United States federal law
whose main provision is to prohibit federal employees (civil servants) from engaging in
partisan campaigns/politics
Define Administrative decentralization correct answers Spreading Elements of the Federal
Government in different parts of the country to provide more efficient service and to adapt
services to the needs of the particular region.
What 5 things constitute the typical bureaucracy? correct answers 1. Specialized jurisdiction
2. Hierarchy of Authority
3. Career structure to provide movement for employees
4. Permanence-stability in the midst of society changing
, 5. Large
What are the 4 main weaknesses of Bureaucracy? correct answers 1. Impersonal
2. Formalistic-very formal
3. Rule Bound-ensure impersonality, help deal w/ outside bolster hierarchical authority
4. Restrictive- restricted by rules and authority structure
What does POSDCORB stand for? correct answers Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing,
Co-Ordinating, Reporting, Budgeting
Know stages of public Administration
According to "Gentlemen"
According to "Spoils"
According to "Merit" correct answers Gentleman: upper class had the baility, education, and
experience to be in gov. Gov was a family business
Spoils: opened up gov to largerpopulation because the people working in gov were benefiting
beneficially
Merits: gov based on skill and accomplishment rather then spoils and nobility of character
Incrementalism correct answers Policy making characterized by a series of decisions, each
instituting modest change
Organization Theory-definition correct answers An attempt to understand how organizations
function and what improves or impairs its ability to accomplish its mission and what
motivates people to work toward goals.
PR Strategic planning process correct answers 1. Assemble & Identify key stakeholders
2. Develop an evaluation plan (goals, methods, questions)
3. Conduct the evaluation (describe program, expectations, resources, operations)
4.Gather evidence
5. Share best practices
6. Data collection
7. Analysis & Surveillance
(PPBS) Planning Programming Budgeting System correct answers Planning- Achieve
program goals
Programming- Alternative goals identified
Evaluation- Cost/benefits are evaluated
Implementation- Best alternatives adopted
Taylorism correct answers Methods of labor management to streamline the process of mass
production in which each worker performs one task.