b/c = because
b/w = between
w/ = with
expt = experiment
ex. = example
Dorsal blastopore lip: mesoderm cells push endoderm cells into blastopore (vegetal side).
(now onto chicken embryo below)
Lecture 5
Tuesday, August 13, 2019 12:40 PM
Gastrulation -> Neurulation: neural tube formation IN VERTEBRATES! (Xenopus)
• The edge of the neural plate forms neural folds which rise toward the midline and fuse.
○ Notochord is derived from chorda-mesoderm, migrates below neural plate.
○ Neural plate is derived from ectoderm, above the notochord and somites.
○ PATTERN: mesoderm is usually below the ectoderm.
• The folds fuse to form the neural tube, which sinks below the epidermis.
• In the trunk region, somites are formed.
○ Dorsal part of somites become dermatome (future dermis).
○ Rest of somite becomes vertebrae, trunk muscles, skeleton, and limbs.
○ FUN FACT: Ventral mesoderm is where future blood cells are derived from.
• In the anterior embryo,
○ The brain is divided (fore, mid, and hind).
○ Precursor placodes form (eye and ears) .
○ 3 brachial arches form. (becomes gills in fish, jaw in humans)
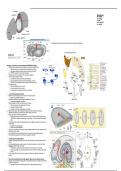
• -> Chick Embryo Development (Chicken)
• Blastoderm: a disc of (multiple cell division) cells which sit on top of the yolk.
○ Blastula (frog): blastoderm (chicken, fly)
• Gastrulation: development of primitive streak and establishment of A/P axis.
○ Streak similar to blastopore in amphibians.
• Posterior marginal zone (PMZ): forms at the junction of the areas.
○ Defines the dorsal side and posterior end of the embryo.
○ Gastrulation is initiated at this site.
○ Area opaca on the sides and area pellucida in the middle.
• Epiblast: embryo proper-- area of blastoderm that gives rise to embryo. (SAME in all mammals)
• Hypoblast: extra-embryonic structures (yolk sac, amnion, allantois, chorion, etc).
• Koller's sickle: anterior movement of primitive streak.
○ Epiblast cells converge on the streak line and move forward. Prospective mesoderm/endoderm cells
(PUSHED INTO) invaginate, spreading anteriorly and laterally. -> forms mesenchymal layer (migrating
cells)!
• Once primitive streak has reached its greatest length, anterior end begins to regress back to posterior end. ->
Henson's Node
○ Equivalent to an organizing center.
○ ZIPPING, AND THEN UNZIPPING.
• As Henson's node regresses, the notochord is formed immediately anterior to it and the mesodermal cells on
either side give rise to somites.
• As the notochord forms, the neural tube starts to form at the anterior end and proceeds posteriorly.
• The head becomes separated from the surface of the epiblast by a head fold.
• -> Mouse Embryo Development (Mouse)
• Fertilization and cleavage (cell division) occurs in the oviduct (the tube thru which the egg passes from the (Still chicken)
ovaries).
• At the 8-cell stage blastomeres undergo compaction, and cells become polarized. -> Morula, ball of cells.
• Blastopore Blastocyst formation (3.5-4 days):
○ Trophectoderm: outlined part of morula that becomes extra embryonic tissue. Ex. placenta
○ Inner cell mass (ICM): part of morula that becomes the embryo. FUN FACT: ES cells are derived from
the ICM.
• We can use these ES cells to birth an in-vitro mouse with a fraction of genotypes/mix of phenotypes. ->
Chimeras
• Cells of early mammalian embryos are highly regulated. (Mouse, but also mammals in general)
• (Cleavage -> Morula formation) Totipotent cells: have the potential to become any cell type in the adult body.
Can become any germ cells.
○ Only totipotent cells are the fertilized egg and the first 4-8 cells produced by its cleavage.