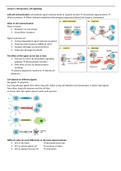
Reactions common to both Aldehydes and Ketones
The difference between an Aldehyde and a Ketone is the position of the C=O (Carbonyl group).
Aldehyde – always on a carbon at the end of the chain
Ketone – Always on a carbon at middle carbon of the chain
1. BOTH Aldehydes and Ketones can be reduced
Aldehyde reduced to Primary Alcohol
Reducing agent = Sodium tetrahydroborate III (NaBH4)
Ketone reduced to Secondary Alcohol
Reduction Oxidisation
Gain of Electrons Loss of Electrons
H
O
H3C C
+ 2[H] H3C C OH
H H
True for all secondary alcohols
Carbonyl + 2[H] ─(NaBH4) Alcohol
CH3CH2CHO + 2[H] CH3CH2CH2OH
Propanal + NaBH4 Propan-1-ol
CH3COCH3 +2[H] CH3CH(OH)CH3
Propanone + NaBH4 Propan-2-ol
2. BOTH Aldehydes and Ketones undergo nucleophilic substitution using HCN
Def.
A nuclophile is an electron pair donor
E.g. NH3 – 1 lone pair
H2O – 2 lone pairs
OH– – 3 lone pairs
Cl– – 4 lone pairs
Therefore nucleophiles attack
E.g. Cδ+=Oδ– 1
Due to a difference in electronegativity the O is
electronegative than the C so attracts the electron
pair more strongly
, NOTE:
C C – A C=C will undergo
C C = electrophillic addition
reactions and the reagents
are added across the double
bond
– A C=O double bond
undergo nucleophillic
addition reactions and the
C reagents are added across
C O = O
the double bond
Mechanism of the reaction between Ethanal and HCN
Conditions: K+CN– = catalyst
Reagents: O
+ HCN(g)
H3C C H
δ+ O δ+ δ–
H3C C H CN
O H
H
Ethanal Intermediate HC C H
O 3
2 Hydroxylpropanenitrile
N C C CN
H3C H
KCN Nitrile group
CN
Mechanism of the reaction between Propanone and HCN
δ+ δ–
H CN
Conditions: K+CN– = catalyst
Reagents: O
O O H
2
H3C C CH3 HC C CH HC C CH
3 3 3 3
Propanone
CN CN
N C 2 Hydroxyl 2 methylpropanenitrile
Intermediate
KCN
, 3. BOTH react with 2,4, Dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4, DNPH)
2,4,DNPH is an orange solution
The reaction is used as a test for the C=O double bond
Reacts to give an orange/yellow precipitate
H3C
H2N C N + H2O
HC C O
3
NH H NH
O O
H
Ethanal + +
+
N N
+ O + O
O N O N Orange/Yellow
2,4, DNPH precipitate
O O
Example exam Q.
Q. How can you distinguish between an Aldehyd and a Ketone? (4 marks)
A. Dissolve in 2,4 DNPH if precipitate is found the C=O bond present
Orange precipitate is purified by recrystalisation
Dry the crystals and heat them until their melting point is found
check the melting point found against data
Identify the exact Aldehyde or Ketone found
Reactions for Aldeydes only
1. ONLY Aldeydes can be oxidised with Acidified Dichromate (H+/Cr2O 72-)
Primary Alcohol Aldehyde Carboxylic Acid
Secondary Alcohol Ketone
Tertiary Alcohol
O H O
H3C C + [O] H C C
3
H H OH
H+/Cr2O72-
Ethanal Acidified Dichromate Ethanoic Acid
, 2. ONLY Aldehydes can react in the Silver mirror test (Tollens Test)
Reagents: Silver nitrate dissolved in Amonnia (Ag+ (NH 3)2 )
Conditions: Hot water bath
If an Aldehyde is present the Silver ion (Ag+) changes to a silver atom (Ag)
Ag+ + 1e– Ag(s)
ion – 46e– atom – 47e–
As the Aldehyde was oxidised the Ag+ gained an electron and was reduced
Aldehydes Carboxylic Acid KetonesNo further reaction
4