IBCLC - Breast Anatomy Exam questions and answers 2024 already graded A+
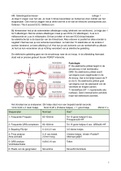
Gigantomastia Extreme growth of the breasts in pregnancy. Very rare. Potential hormonal cause. Milk Ejection Reflex Causes contraction of the myoepithelial cells. Requires oxytocin. Lactocytes Specialized epithelial cells that line the interior of the alveolus. Absorb nutrients, immunoglobulin and hormones from the blood to compose milk. Serum Placental Lactogen Aids in areolar growth. Oxytocin Secreted from posterior pituitary. Responsible for milk ejection. Rises in a pulse pattern within 1 minute of sucking and returns to baseline in 6 minutes. Contracts the uterus. Inhibited by pain, fear, stress, fatigue, alcohol and induction of labor. Prolactin Secreted from anterior pituitary. Responsible for milk production. Aids in nipple growth. Pregnancy levels 10-20ng; lacation levels 200-400ng. Progesterone Placental expulsion causes dramatic drop. Elevation inhibits prolactin. Causes glandular tissue to expand and the growth of lobules, lobes and alveoli. Estrogen Stimulates duct growth. Tail of Spence Mammary gland tissue that projects into the axillary region. Stroma Supporting tissues of the breast. Includes connective tissue, fat, blood vessels, nerves and ligaments. Lobes Clusters of lobules filled with alveoli. The breast contains 15-25 of these. Polythelia Extra nipples Polymastia Extra breast tissue Hyperthelia A nipple with no mammary tissue Hypoplasia Insufficient glandular tissue Common Nipple Protrudes slightly when at rest and becomes erect when stimulated Mammary Gland Development Cycle 1. Mammogenesis 2. Lactogenesis 3. Galactopoiesis 4. Involution Milk Synthesis Occurs in lactocytes. Controlled independently by each breast. Ranges from 17-33 ml/hour. Adipose Tissue Tissue made of fat Maternal Condition that Delay Lactogenesis Primiparity, Maternal age >30, cesarean birth, long stage II labor, fluid load in labor, diabetes, epidural, obesity, PCOS, Ovarian cysts, placenta retention, Sheehan's Syndrome, stress, prolactin deficiency, breast surgery Three Factors necessary for lactation 1. oxytocin from posterior pituitary 2. milk removal 3. prolactin from anterior pituitary Cooper's Ligaments Connective tissue in the breast that helps maintain structural integrity. Feedback Inhibitor of Lactation (FIL) Small protein present in milk which increases in concentration when the breast is full Full breasts = more inhibition of milk production Frequent emptying = less inhibition of milk production Nipple Translocation Surgery in which the nipple is removed, breast tissue reduced and nipple reattached. Inferior Pedicle Technique Breast reduction surgery in which some portion
Escuela, estudio y materia
- Institución
- IBCLC
- Grado
- IBCLC
Información del documento
- Subido en
- 3 de abril de 2024
- Número de páginas
- 5
- Escrito en
- 2023/2024
- Tipo
- Examen
- Contiene
- Preguntas y respuestas
Temas
-
ibclc breast anatomy exam questions and answers
Documento también disponible en un lote